Overview
This article delineates five essential steps for effectively utilizing a Self-Directed IRA (SDIRA) to purchase real estate:
- Selecting a custodian
- Completing an application
- Funding the account
- Reviewing the setup
- Maintaining documentation
These steps are vital as they ensure compliance with regulations and maximize investment potential. By following these guidelines, investors can diversify their portfolios and seize various real estate opportunities, all while adeptly navigating potential risks and tax implications. Understanding these processes not only empowers investors but also enhances their ability to make informed decisions in the dynamic real estate market.
Introduction
In the realm of retirement planning, Self-Directed IRAs (SDIRAs) are gaining traction as a versatile investment vehicle that empowers individuals to take control of their financial futures. Unlike traditional retirement accounts, which limit investment choices to stocks and bonds, SDIRAs open the door to a diverse array of assets, including real estate and precious metals. As investors increasingly seek ways to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on alternative investments, understanding the intricacies of SDIRAs becomes paramount.
This guide delves into the essential steps and strategies for leveraging SDIRAs effectively, ensuring that investors can maximize their retirement potential while minimizing risks.
Understand Self-Directed IRAs
A Self-Directed IRA (SDIRA) is a specialized individual retirement account that significantly expands your asset choices beyond traditional stocks and bonds. Unlike conventional IRAs, which restrict options to stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, a self directed ira to buy real estate enables allocations in real estate, precious metals, and various alternative assets. This flexibility not only facilitates greater diversification but also opens the door to potentially higher returns.
To fully leverage the advantages of an SDIRA, it is crucial to understand its framework, including the role of custodians, the categories of assets permitted, and the associated tax benefits. For instance, earnings from assets held within an SDIRA enjoy tax-deferred status until withdrawal, and contributions may qualify for tax deductions, particularly for individuals below certain income thresholds.
Familiarity with these elements empowers you to make informed financial decisions, particularly in light of current market dynamics. Given that property values can fluctuate significantly during economic downturns—potentially decreasing by 10% to 50%—having a strategic asset option like a self directed ira to buy real estate can be invaluable. By 2025, it is projected that approximately 35% of investors will be utilizing SDIRAs for alternative assets, underscoring a growing trend toward diversification in retirement planning. This trend accentuates the importance of professional guidance; as one investor noted, "This is advanced learning and based on discussions I had with three of the leading property attorneys in the country, along with my own personal experience." Understanding these concepts will equip you to navigate the complexities of property financing through a self directed ira to buy real estate successfully.
Set Up Your Self-Directed IRA
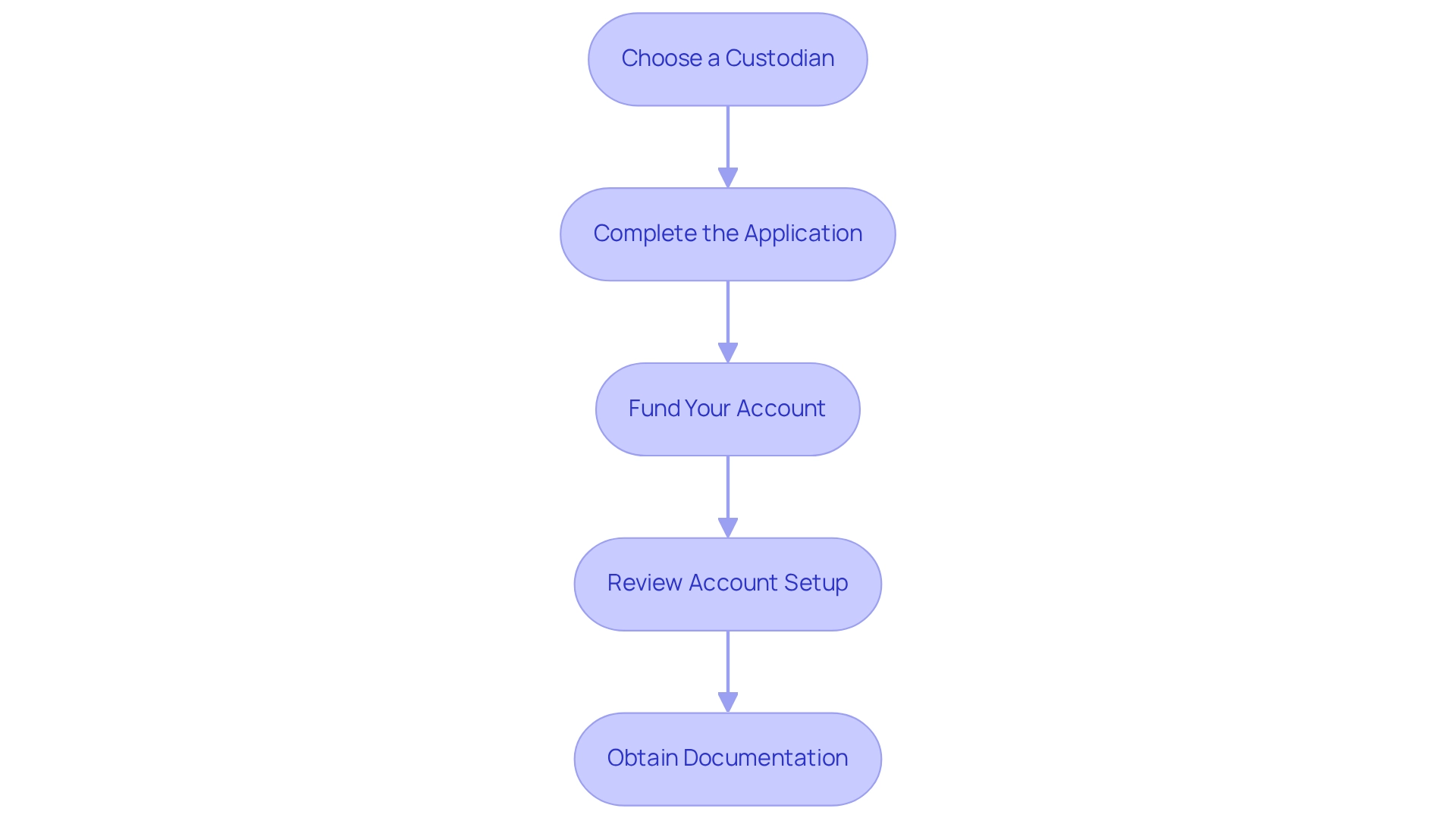
Setting up your Self-Directed IRA involves several key steps to ensure a smooth process:
- Choose a custodian: Selecting a custodian specializing in a self-directed IRA to buy real estate is crucial, particularly one with a strong reputation and expertise. This choice is vital, as custodians do not assess the validity of assets, placing the onus on you to conduct thorough research. As Daniel Hanlon, senior vice president of Midland Trust, states, "Self-directed IRA custodians do not assess the legitimacy or quality of an asset." It’s the shareholder’s responsibility to study purchases, asset managers, and other trusted partners with the same level of care.
- Complete the Application: Fill out the application forms provided by your chosen custodian. This usually necessitates personal information and details about your financial preferences.
- Fund Your Account: Transfer funds from an existing retirement account or make a new contribution. Be mindful of contribution limits and potential tax implications to avoid penalties.
- Review Account Setup: After funding your account, review the setup with your custodian to confirm that everything is correctly established before making any contributions.
- Obtain Documentation: Maintain all documentation related to your Self-Directed IRA setup. This paperwork is essential for future transactions and compliance with IRS regulations.
While Self-Directed IRAs provide a wider array of options for assets, they also come with significant risks and drawbacks that you should be aware of before proceeding. In 2025, the typical fees for custodians of Self-Directed IRAs vary, making it wise to compare expenses among reputable custodians, ensuring you assess them based on their standing and expertise in property holdings. Additionally, statistics indicate a growing trend in the establishment of Self-Directed IRAs annually, highlighting their increasing popularity among investors. With more than 30,000 subscribers, Zero Flux serves as an essential resource, offering insights into the intricacies of property financing through a data-oriented approach.
Explore Real Estate Investment Options
Once your self directed ira to buy real estate is established, a range of property financing choices becomes available:
- Residential Properties: Investing in single-family homes or multi-family units can yield rental income and long-term appreciation. With millennials leading the home-buying market, this segment is particularly promising, especially as rising rental prices create demand for rental properties.
- Commercial Real Estate: Opportunities in office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial properties often feature longer lease terms and the potential for higher returns. This sector is increasingly attractive as businesses seek stability amid fluctuating economic conditions. Notably, 36.25% of individuals believe that Trump's strategies for inflation and tariffs might adversely affect market recovery in 2025, which could influence financial choices in this sector.
- Property Trusts (REITs): For individuals favoring a more passive strategy, REITs provide an opportunity to invest in varied property portfolios without the necessity for direct management. This option allows investors to benefit from real estate market growth while minimizing hands-on involvement.
- Raw Land: Purchasing undeveloped land can be speculative but may appreciate significantly over time, especially in areas poised for development. This category of funding necessitates thoughtful evaluation of location and future growth potential.
- Real Estate Partnerships: Collaborating with other investors can enhance purchasing capacity for larger endeavors, such as commercial properties or development projects. This approach not only diversifies risk but also leverages collective expertise in property management, making it essential to understand the options available with a self directed ira to buy real estate as the real estate landscape evolves.
Present trends suggest a movement towards residential assets, with average rental earnings from residential properties in SDIRAs demonstrating encouraging returns. Moreover, persistent inventory shortages in the market, caused by homeowners' hesitation to sell in a high-interest-rate environment, further highlight the significance of strategic financial decisions. The worldwide luxury property market was assessed at $8.52 billion in 2018, emphasizing the opportunity for high-value ventures within the sector. Rich Fettke's viewpoint on wealth underscores that genuine prosperity includes both monetary assets and the liberty to live life according to personal choices, urging investors to consider their portfolios from a broader perspective. Lastly, careful property management is essential to maximize tax advantages, and the shift to crowdfunding signifies a profound change in the funding landscape, previously dominated by institutional investors.
Navigate Rules and Regulations
Navigating the rules and regulations surrounding self-directed IRAs (SDIRAs) is essential for ensuring compliance and maximizing investment potential. Understanding the intricacies of these regulations can significantly impact your investment success.
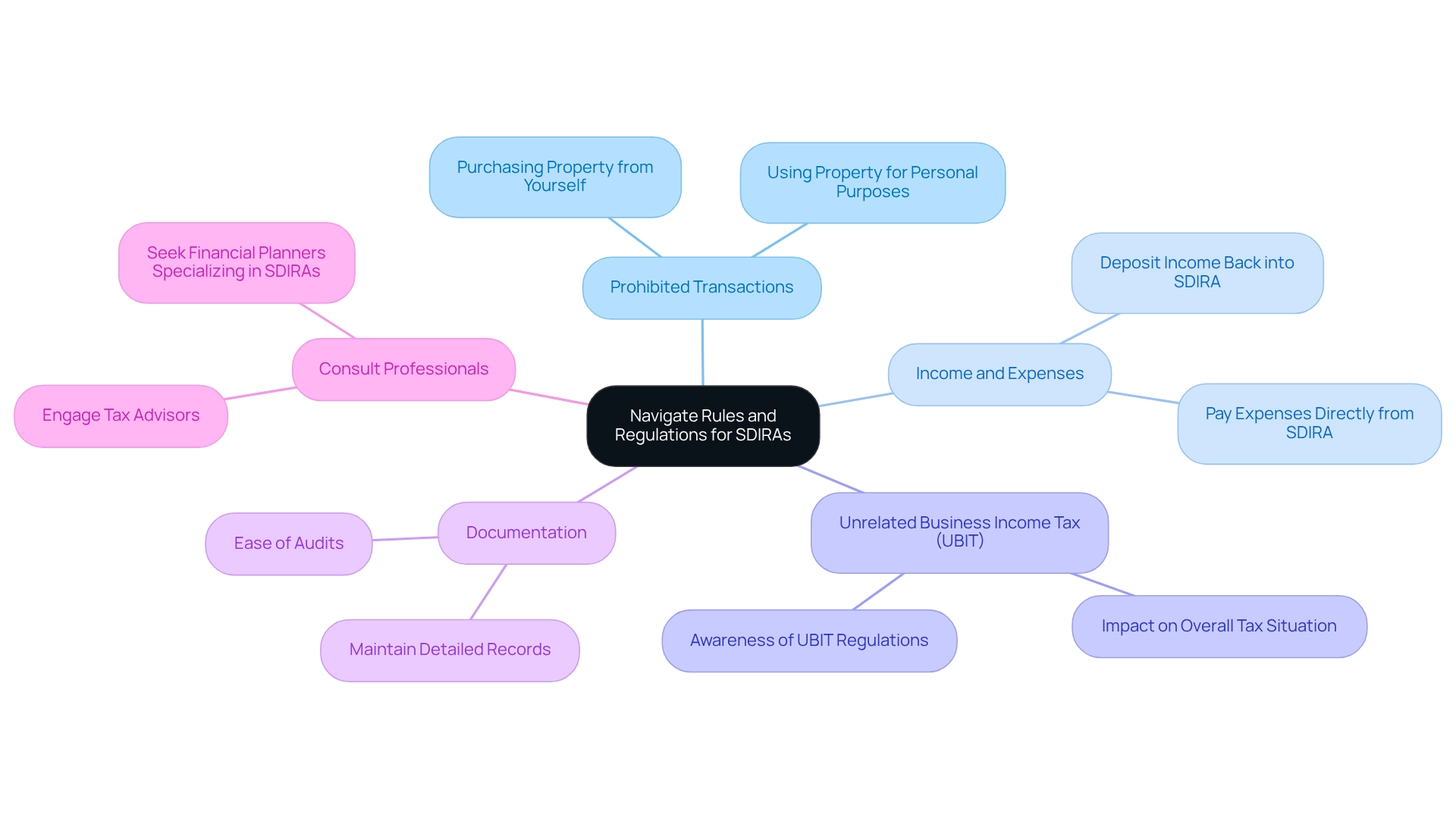
- Prohibited Transactions: Certain transactions are strictly prohibited, such as purchasing property from yourself or using the property for personal purposes. Grasping these restrictions is crucial to avoid penalties that could undermine your investment strategy.
- Income and Expenses: All income generated from the property must be deposited back into the SDIRA, while all related expenses should be paid directly from the SDIRA. This practice is vital to maintain the tax-advantaged status of your account, ensuring your investments continue to grow without unnecessary tax burdens.
- Unrelated Business Income Tax (UBIT): Investments in specific types of businesses may trigger UBIT, impacting your overall tax situation. Awareness of this tax is vital for effective financial planning. Alarmingly, a significant percentage of SDIRA investors remain unaware of UBIT regulations, underscoring the urgent need for education in this area.
- Documentation: Maintaining detailed records of all transactions and communications related to your SDIRA holdings is essential for compliance and can ease audits. This diligent practice not only protects your assets but also enhances transparency, fostering trust in your financial dealings.
- Consult Professionals: Engaging with a tax advisor or financial planner who specializes in SDIRAs can provide invaluable guidance in navigating the complex regulatory landscape. Their expertise can help you make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls. As Thomas W. Abendroth, a partner in the field, aptly states, "The last point in the preceding paragraph, full taxation of the IRA, should serve as sufficient motivation to exercise caution when using a self-directed IRA."
Comprehending these essential rules and guidelines is vital for any investor aiming to use a self-directed IRA to buy real estate. With over 30,000 subscribers, Zero Flux emphasizes the importance of staying informed on financial matters, ensuring that investors are equipped with the knowledge needed to navigate these complexities effectively. Furthermore, Zero Flux's commitment to quality content not only enhances subscriber engagement but also positions it as a trusted resource for navigating self-directed IRA regulations.
Implement Effective Investment Strategies
To implement effective investment strategies with your self-directed IRA to buy real estate, consider the following approaches:
- Diversification: Reduce risk by distributing your resources across various property types, including residential, commercial, and undeveloped land. This strategy not only safeguards your portfolio but also capitalizes on different market segments, enhancing your overall investment resilience.
- Market Research: Conduct comprehensive market research to uncover emerging trends and opportunities. A solid understanding of local dynamics can significantly enhance your financial decisions, leading to higher success rates. Techniques such as analyzing local sales data, monitoring zoning changes, and utilizing technology-driven tools can provide valuable insights that inform your strategy.
- Long-Term Planning: Prioritize long-term growth over immediate gains. Properties typically appreciate in value over time, and a patient approach can yield significant returns. As Mark Twain famously expressed, 'Buy land, they’re not making it anymore,' highlighting the timeless value of land acquisition.
- Leverage Financing: Consider utilizing a self-directed IRA to buy real estate through non-recourse loans. This approach allows you to leverage your SDIRA funds while protecting your personal assets from potential risks associated with real estate. As illustrated in the case study on AI's role in financial planning, technology can enhance portfolio management and provide personalized financial advice, simplifying the navigation of financing options.
- Regular Review: Consistently review your investment portfolio and adjust your strategies based on performance and market conditions. Staying informed about market shifts and trends empowers you to make timely and effective decisions. Investors should also be mindful of waiting for more attractive entry points in speculative sectors, as this can significantly impact long-term success.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of Self-Directed IRAs (SDIRAs) is crucial for investors aiming to diversify their retirement portfolios and capitalize on alternative investments. These accounts present a unique opportunity to extend beyond traditional stocks and bonds, allowing for investments in real estate, precious metals, and other assets that can potentially yield higher returns. The process of establishing an SDIRA necessitates careful selection of a custodian, thorough research, and adherence to regulatory guidelines to ensure compliance and maximize investment potential.
As the real estate investment landscape evolves, various options such as residential properties, commercial real estate, and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) offer unique opportunities for growth. Investors must navigate the accompanying rules and regulations, including prohibited transactions and tax obligations, to fully leverage the benefits of their SDIRA. Engaging with financial professionals can provide invaluable insights and help avoid common pitfalls, ensuring a well-informed approach to investment decisions.
Ultimately, the key to successful SDIRA investment lies in effective strategies that encompass diversification, market research, and long-term planning. By staying informed and adaptable, investors can harness the full potential of their Self-Directed IRAs, paving the way for a secure financial future. Embracing these strategies not only enhances individual investment outcomes but also contributes to a broader trend of empowered, self-directed retirement planning that aligns with personal financial goals.




