Overview
Economic indicators are pivotal for success in retail commercial real estate, offering vital insights into economic performance, consumer behavior, and market trends. These insights empower investors to make informed decisions. Understanding metrics such as:
- GDP
- Unemployment rates
- Consumer spending
not only aids in evaluating investment opportunities but also enables investors to adapt their strategies to the shifting economic landscape. This adaptability significantly enhances their chances of success.
Introduction
In the intricate world of retail commercial real estate, understanding economic indicators is paramount for investors navigating market fluctuations and seizing lucrative opportunities. These vital metrics, ranging from Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to consumer spending habits, offer a lens through which the health of the retail sector can be assessed. As economic landscapes shift, the interplay between consumer confidence and retail performance becomes increasingly evident. This relationship influences everything from leasing strategies to investment decisions.
This article delves into the significance of these indicators, providing insights into how they can inform strategic planning and enhance investment outcomes in a competitive market. By examining key trends and the implications of economic data, stakeholders can better position themselves for success in the dynamic realm of retail real estate. Are you prepared to leverage these insights for your investment strategies?
Understanding Economic Indicators in Retail Commercial Real Estate
Economic indicators are vital statistical metrics that illuminate the economic performance of specific regions or sectors, particularly within retail commercial real estate. For investors and stakeholders, these indicators are essential for evaluating economic conditions and making informed decisions. Key indicators include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Unemployment rates
- Individual spending
- Inflation rates
Understanding these metrics is crucial for assessing potential investment opportunities and predicting market trends. For instance, a growing GDP typically signals increased consumer expenditure, which can lead to heightened sales in stores and subsequently elevate the demand for commercial spaces. In 2022, multifamily rental properties demonstrated a robust occupancy rate of approximately 95%, reflecting strong demand in the housing market that can also influence commercial dynamics.
Moreover, the current financial landscape indicates that the hospitality sector remains stable, with hotel occupancy rates at 63%. Importantly, average daily rates and revenue per available room have surpassed pre-pandemic levels, suggesting a recovery that could positively impact nearby shopping environments.
Investors should also consider the implications of economic indicators on retail commercial real estate investment strategies. The commercial space sector has remained exceptionally tight, with available leasing area consistently below 5% in recent years. Demand is rising, exerting additional pressure on the industry, especially given the limited new supply.
Over the past 12 months, net deliveries totaled just over 30 million square feet, which is about 40% below the 10-year average. These conditions suggest that the fundamentals of the commerce sector are expected to remain constrained, making it imperative for investors to stay attuned to these financial signals.
In summary, grasping financial indicators not only aids in navigating the complexities of the retail commercial real estate market but also enhances the ability to capitalize on emerging opportunities. As the landscape evolves, remaining informed about these metrics will be crucial for success in retail commercial real estate investment.
Key Economic Indicators to Monitor for Retail Success
Several key economic indicators play a crucial role in determining retail success:
- Customer Confidence Index (CCI): This index measures public optimism regarding their financial future. A high CCI often correlates with increased buyer spending, which is essential for business growth. Recent trends indicate a slight decline in public optimism, with only 2.1% of respondents expecting prices to decrease in March, reflecting a 0.3 percentage point drop from the previous month. As noted by Stephanie Guichard, Senior Economist at Global Indicators, "Individuals are less optimistic about the future in February," emphasizing the cautious perspective among buyers that can influence market performance. Upcoming publications of public confidence statistics are planned for April, May, June, and July 2025, offering timely insights into current economic conditions. It's also important to note that the survey method has evolved over the years, with the current method combining mail and online responses since October 2018, which enhances the reliability of the CCI data.
- Sales Data: Tracking monthly sales figures is essential for comprehending spending patterns of buyers. In 2025, sales data has shown fluctuations that can indicate shifts in consumer behavior, offering investors insights into market dynamics. For instance, an increase in sales can signify a strong economy, encouraging investors to explore new opportunities in commercial properties.
- Unemployment Rate: A lower unemployment rate generally results in higher disposable income, which can boost sales in stores. As more individuals secure jobs, their purchasing power rises, directly benefiting retail establishments. Monitoring employment trends can assist investors in predicting changes in spending habits.
- Inflation Rate: Grasping inflation is essential for investors as it influences buying power. Rising inflation can erode disposable income, leading to changes in spending habits. Investors must adjust their strategies accordingly to mitigate risks associated with inflationary pressures.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates greatly affect borrowing costs and spending habits. Reduced interest rates can encourage commercial growth by making financing more accessible for both consumers and businesses. As interest rates vary, investors ought to evaluate how these shifts could affect sales and overall economic conditions.
By examining these financial indicators, investors can make educated choices that correspond with current trends, ultimately improving their success in commercial real estate. The method employed by Zero Flux, a data-focused real estate newsletter, illustrates how gathering vital industry insights can assist investors in maneuvering through the intricacies of the commercial environment.
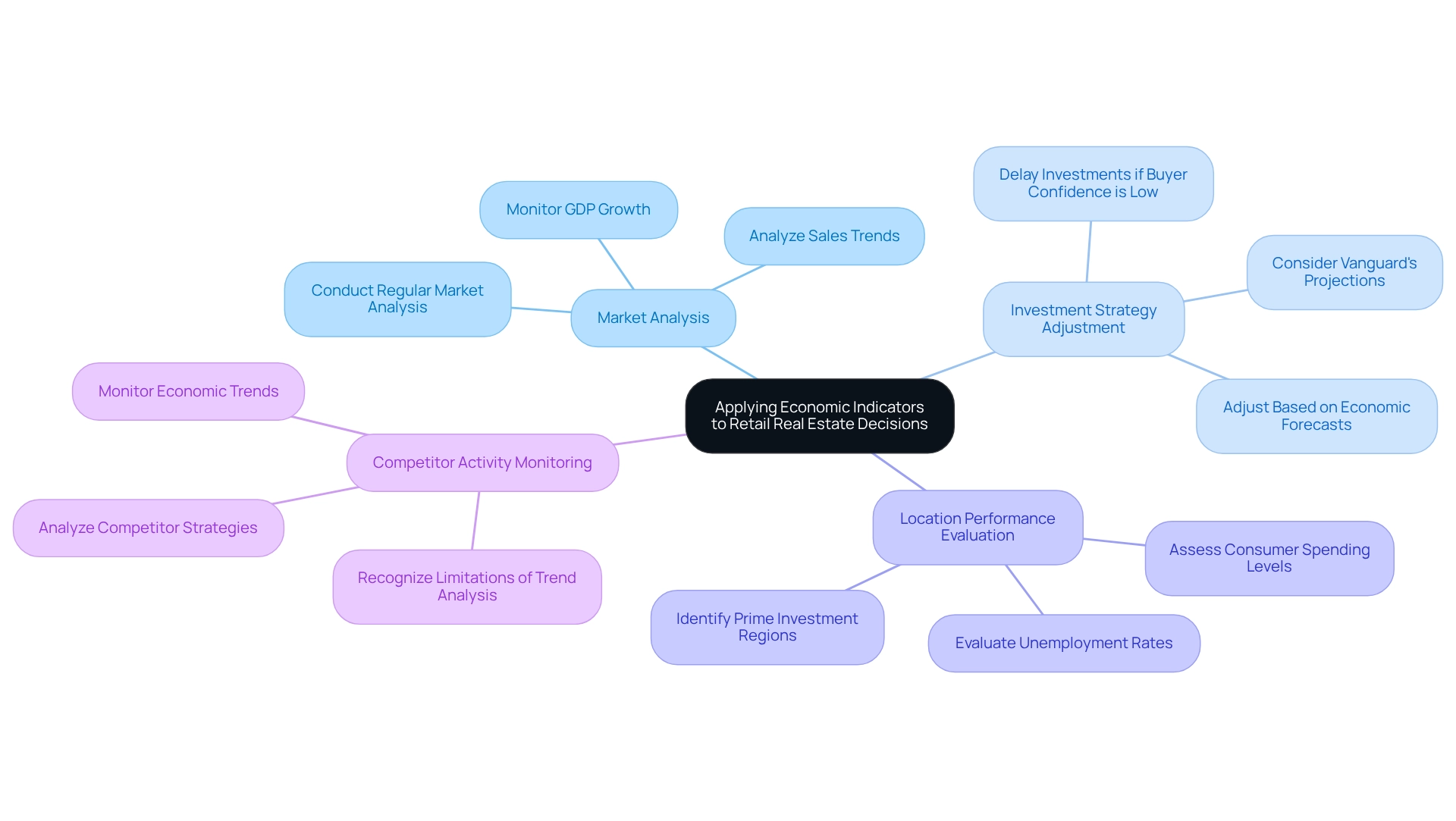
Applying Economic Indicators to Inform Retail Real Estate Decisions
To effectively utilize financial indicators in commercial real estate decisions, investors should consider the following strategies:
- Conduct Regular Market Analysis: Investors should leverage financial indicators to analyze market trends and identify potential investment opportunities. For instance, a rise in sales within a specific area may indicate a growing demand for commercial space, suggesting a favorable environment for investment. Additionally, with real gross domestic product (GDP) rising at an annual rate of 2.3 percent in the fourth quarter of 2024, this growth further suggests a positive outlook for retail investments.
- Adjust Investment Strategies: Economic forecasts play a crucial role in shaping investment strategies. If buyer confidence is reported to be low, it may be prudent to delay new investments until market conditions show signs of improvement, thereby reducing risk. As noted by Vanguard, forecasts concerning investment results are theoretical and do not guarantee future outcomes, underscoring the necessity for careful decision-making based on financial indicators.
- Evaluate Location Performance: Economic indicators are essential for assessing the viability of specific locations. Regions characterized by low unemployment rates and high consumer spending generally offer more advantageous conditions for commerce investments, making them prime targets for investors.
- Monitor Competitor Activity: Keeping an eye on economic trends can provide valuable insights into competitor strategies. By understanding these trends, investors can position themselves favorably in the industry, ensuring they remain competitive and adaptable to shifts in the commercial environment. However, it is crucial to recognize the limitations of trend analysis, as highlighted in the case study on this topic. Relying exclusively on historical data may overlook essential elements influencing market performance and can yield varying outcomes depending on the statistical techniques employed.
By methodically implementing these strategies, investors can enhance their decision-making processes and navigate the complexities of the commercial real estate market in 2025.
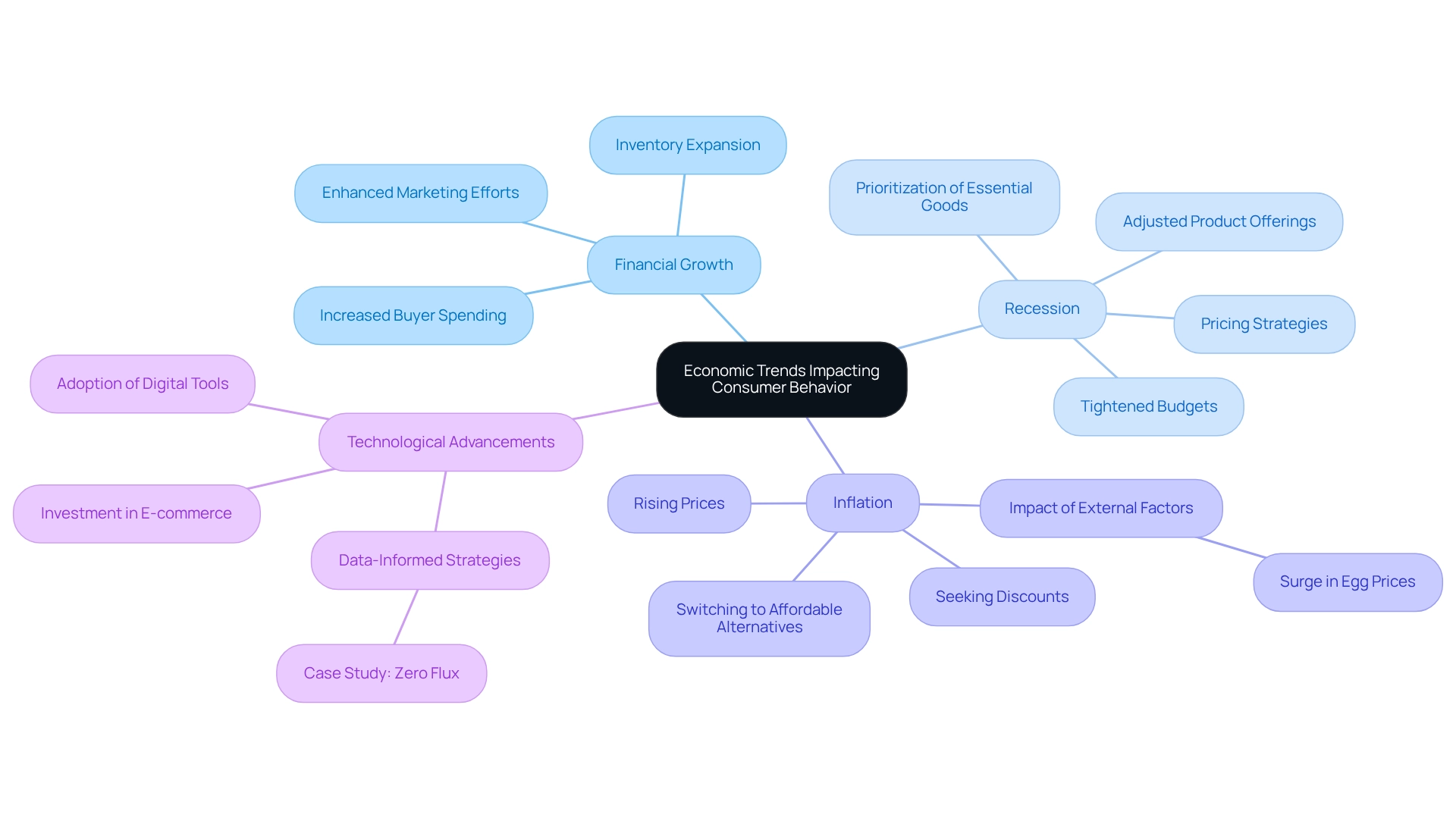
The Impact of Economic Trends on Consumer Behavior in Retail
Economic trends play a crucial role in shaping buyer behavior within the sales sector. Understanding these dynamics empowers retailers to make informed decisions and optimize their strategies. Key trends include:
- Financial Growth: During periods of financial expansion, buyer spending generally rises, leading to increased retail sales. Retailers can leverage this growth by expanding their inventory and enhancing marketing efforts to attract more customers.
- Recession: Conversely, during economic downturns, individuals often tighten their budgets, prioritizing essential goods over luxury items. Retailers must adapt by adjusting their product offerings and pricing strategies to remain competitive in a more price-sensitive market. For instance, with 12% of individuals using GLP-1 medications, discretionary spending is affected, resulting in changes in purchasing priorities.
- Inflation: Rising prices can significantly alter buyer behavior, prompting shoppers to seek discounts or switch to more affordable alternatives. Recent news highlights the surge in egg prices due to the culling of over 30 million chickens to combat bird flu, illustrating how external factors can influence purchasing power. Retailers should closely monitor inflation trends and adjust their pricing strategies to align with consumer expectations and maintain sales. As Yelena Shulyatyeva, a Senior U.S. Economist, noted, barring de-anchoring of longer-term inflation expectations, the negative impact on growth is likely to overwhelm the impact of higher inflation, which may lead to policy rate reductions in the latter half of 2025.
- Technological Advancements: Economic conditions also influence the pace of technological adoption in retail. For example, during times of financial growth, retailers are more inclined to invest in e-commerce platforms and digital tools to improve customer experiences and optimize operations. The case analysis of Zero Flux illustrates how a data-informed strategy can assist retailers in adapting to financial shifts, emphasizing the significance of being aware of industry dynamics.
By remaining attentive to these financial signals, retailers can more effectively address the intricacies of buyer behavior, ensuring they stay responsive to shifts and client needs.
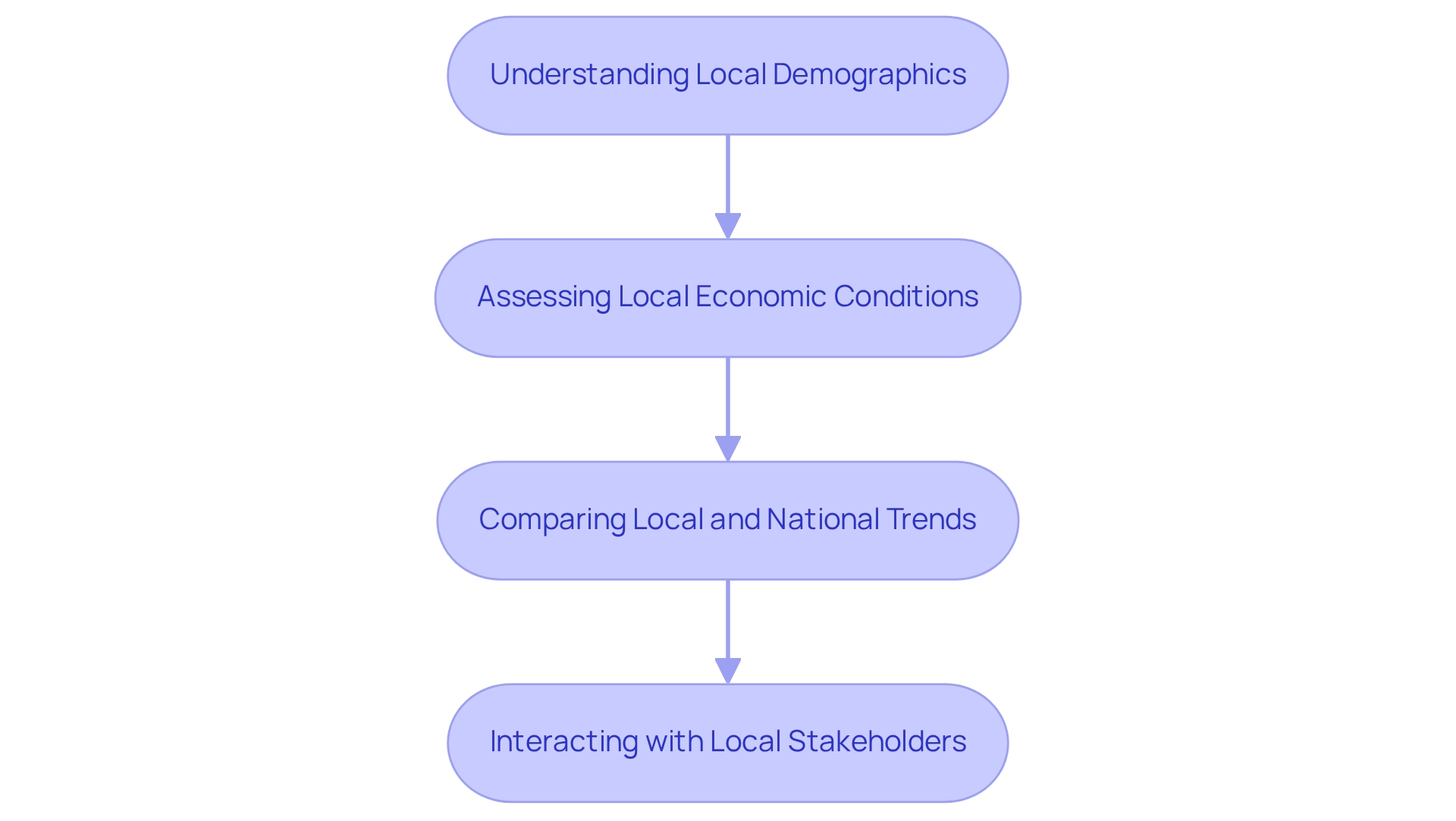
Integrating Local Market Analysis with Economic Indicators
Combining local market analysis with economic indicators is crucial for making informed choices in commercial real estate. This process involves several key components:
- Understanding Local Demographics: A thorough analysis of local demographics—including age distribution, income levels, and population growth—is essential. This data not only assists in forecasting consumer behavior but also provides insights into the demand for various commercial spaces. For instance, areas with a younger population may exhibit a greater demand for fashionable shopping venues, while regions with older demographics might prefer convenience stores and essential services. According to Statista, U.S. customers predominantly buy fashion items, with clothing constituting 43% of their purchases and shoes accounting for 33%. This insight underscores the significance of comprehending local demographics in shaping consumer offerings.
- Assessing Local Economic Conditions: Evaluating local economic indicators such as employment rates, business growth, and consumer spending patterns is vital. These factors directly influence market performance; for instance, a rise in employment rates typically associates with increased disposable income, resulting in higher sales. Notably, 91% of customers are likely to repurchase after a positive customer service experience, highlighting the importance of customer service in driving sales. Comprehending these dynamics enables investors to assess the condition of the consumer sector in specific areas.
- Comparing Local and National Trends: While national economic indicators provide a broad overview of economic conditions, local trends can reveal unique opportunities or challenges. Investors should analyze local data alongside national trends to identify discrepancies that may indicate potential investment opportunities. For example, if nationwide sales are decreasing but a particular local area is thriving, this might signal a profitable investment opportunity. Furthermore, the anticipated expansion of the AI sector in commerce, expected to reach $54.92 billion by 2023, with a yearly growth rate of 18.6% from 2024-2033, further emphasizes the technological progress affecting investment choices in commerce.
- Interacting with Local Stakeholders: Establishing connections with local business proprietors, community leaders, and development organizations can provide invaluable insights into conditions and consumer preferences. These stakeholders often possess firsthand knowledge of emerging trends and can offer context that data alone may not reveal. Engaging with them enhances an investor's understanding of the local landscape, leading to more strategic investment decisions. Notably, from 2017 to 2021, more than half of U.S. businesses had one owner, with women-owned businesses being more likely than male-owned businesses to have a single owner. This context on local business dynamics can significantly influence market conditions.
By concentrating on these areas and integrating pertinent statistics and case studies, investors can effectively merge local market analysis with economic indicators, positioning themselves to seize opportunities in a dynamic market.
Strategies for Leveraging Economic Indicators in Retail Investments
To effectively leverage economic indicators in retail investments, implement the following strategies:
- Establish a Comprehensive Monitoring System: Develop a robust system to consistently track key financial indicators that align with your investment strategy. This involves establishing notifications for major changes in public confidence, retail sales figures, and other pertinent metrics to remain updated on market dynamics. Effective monitoring can lead to improvements in order fulfillment by 10-20%, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
- Invest in Advanced Data Analytics Tools: Utilize sophisticated data analytics tools designed to analyze market trends and buyer behavior patterns. As Quantive StrategyAI states, "Quantive StrategyAI turns raw, unstructured data into actionable insights." These tools can transform raw data into actionable insights, enabling you to make informed investment decisions based on real-time information.
- Engage in Scenario Planning: Utilize financial indicators to conduct thorough scenario planning. For example, evaluate how variations in interest rates might influence consumer spending patterns, enabling you to modify your investment approach proactively in reaction to possible economic changes.
- Collaborate with Industry Experts: Build connections with other real estate professionals and analysts to share insights and strategies concerning market indicators. Networking within the industry can provide diverse perspectives that enhance your decision-making process and keep you ahead of market trends.
- Monitor Economic Indicators for Retail Investment Strategies in 2025: As we move into 2025, focus on best practices for monitoring economic indicators that directly influence retail investments. This includes tracking metrics such as employment rates, inflation, and consumer spending trends to refine your investment approach. The shift in industries towards generating actionable insights highlights the significance of these strategies in the present business environment.
- Utilize Data Analytics for Financial Trend Analysis: Employ data analytics tools specifically tailored for analyzing financial trends in commerce. These tools can help identify patterns and forecast future market conditions, providing a competitive edge in your investment strategy. Companies like Tesla are leading the way in hyperautomation, achieving significant cost reductions and efficiency improvements in production through the integration of AI and IoT technologies.
By applying these strategies, you can enhance your ability to navigate the intricacies of retail commercial real estate, ensuring that your investment choices are driven by the most relevant financial indicators.
Challenges and Limitations of Using Economic Indicators in Retail Real Estate
While economic indicators serve as essential tools for investors, notable challenges and limitations warrant careful consideration.
Lagging Indicators: Many indicators are classified as lagging, primarily reflecting past performance rather than current market conditions. This characteristic can mislead investors who rely solely on these metrics for decision-making. For instance, the recent drop of 7.4 percent in the US Leading Economic Index® in March underscores the importance of not depending solely on historical data when evaluating future investment opportunities. Such a decline may suggest a potential slowdown in activity that could influence consumer performance.
Data Interpretation: Misinterpretation of economic data poses a considerable risk. Investors must diligently understand the context and implications of the indicators they analyze. For example, the slight 0.2 percent decrease in Coincident Manufacturing and Trade Sales indicates a modest pullback in business activity. This decline may signal caution in consumer spending, prompting investors to reassess their positions in the retail sector if not understood correctly.
Market Volatility: Economic conditions can shift rapidly, and indicators may fail to predict future trends accurately. Investors should remain agile and prepared to adjust their strategies in response to evolving market dynamics. The upcoming release of economic indexes on March 20, 2025, will be crucial for assessing current conditions, as it may provide insights into the economy's trajectory. Investors must exercise caution regarding overreacting to single data points and should consider the broader context of these updates.
Overreliance on Quantitative Data: An excessive focus on quantitative data can lead to neglecting qualitative factors that significantly influence commercial success. Factors such as consumer sentiment and brand loyalty are essential in influencing economic outcomes and should be incorporated into investment analyses to offer a more comprehensive perspective on potential opportunities.
Understanding these challenges is vital for making informed investment decisions in retail commercial real estate. By acknowledging the limitations of delayed financial indicators and the significance of precise data analysis, investors can more effectively navigate the intricacies of the market. As noted by Justyna Zabinska-La Monica, Senior Manager of Business Cycle Indicators, "We currently forecast that real GDP for the US will expand by 2.3% in 2025, with stronger growth in the first half of the year," highlighting the need for investors to stay informed about economic trends.
Additionally, resources like Zero Flux can provide valuable insights, assisting real estate professionals in making data-driven decisions in a rapidly changing environment.
Conclusion
Understanding and leveraging economic indicators is crucial for success in retail commercial real estate investment. Key metrics such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), consumer confidence, and retail sales data serve as essential tools for navigating market fluctuations. These indicators provide insights into current market conditions and aid investors in forecasting future trends, assessing potential opportunities, and refining their investment strategies.
Moreover, integrating local market analysis with broader economic indicators significantly enhances decision-making processes. By examining demographics, local economic conditions, and engaging with community stakeholders, investors can uncover unique opportunities that may not be visible through national data alone. This combination of local insight and economic analysis empowers investors to make more informed, strategic choices in a competitive landscape.
Ultimately, the dynamic relationship between economic indicators and retail performance underscores the importance of staying informed and adaptable. As market conditions evolve, those who effectively monitor and interpret these indicators will be better equipped to navigate challenges and seize opportunities, ensuring long-term success in the retail real estate sector. Embracing a proactive approach to economic analysis will enable investors to thrive amidst the complexities of the retail landscape.




