Overview
The article underscores the significance of environmental reports in real estate investments, highlighting their crucial role in evaluating ecological risks that could impact property value and investment viability. By detailing the various types of environmental site assessments and the essential components of these reports, it establishes a foundation for understanding their importance. Furthermore, it illustrates how the integration of sustainability insights into investment strategies can not only enhance financial outcomes but also mitigate potential risks, ultimately influencing investment decisions.
Introduction
Understanding the intricate relationship between environmental reports and real estate investments is increasingly crucial in a world where sustainability dominates financial decision-making. These reports not only unveil potential ecological hazards but also highlight opportunities that can enhance property value and bolster investor confidence. As regulatory pressures mount and the market evolves, investors must navigate the complexities of environmental assessments effectively.
How can they safeguard their investments and maximize returns in this challenging landscape? This question underscores the necessity of informed decision-making in the realm of real estate investment.
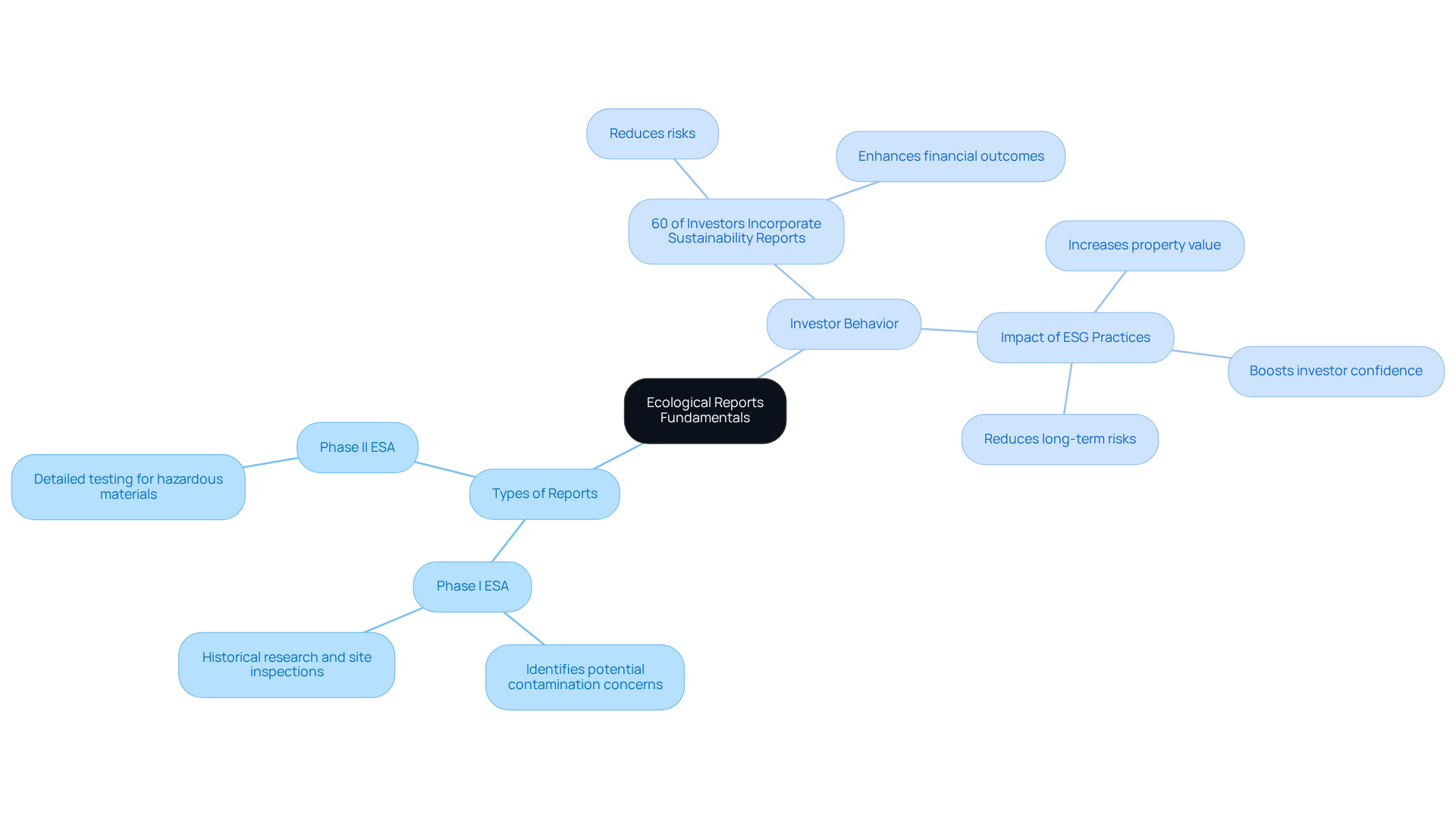
Clarify Environmental Report Fundamentals
Ecological reports serve as essential instruments for evaluating potential ecological hazards associated with a location. These comprehensive documents assess critical factors such as soil, water, and air quality, alongside historical land use, unveiling hidden liabilities that could significantly impact property value and investment viability. Among the key types of ecological reports are Phase I and Phase II Site Assessments (ESAs).
- Phase I ESAs identify potential contamination concerns through historical research and site inspections.
- Phase II ESAs involve more detailed testing to confirm the presence of hazardous materials.
Notably, around 60% of investors integrate sustainability reports into their decision-making processes, indicating a growing acknowledgment of their significance in reducing risks and enhancing financial outcomes. As real estate increasingly faces scrutiny regarding sustainability and environmental impact, understanding the environmental report real estate is essential for making informed financial decisions. Furthermore, with the rise of regulatory pressures on ESG reporting, investors must consider how these factors, such as the environmental report real estate, influence valuation and investment strategies.
As highlighted by industry specialists, 'Integrating ESG practices has been shown to enhance property value, investor confidence, financial returns, and reduce long-term uncertainty.
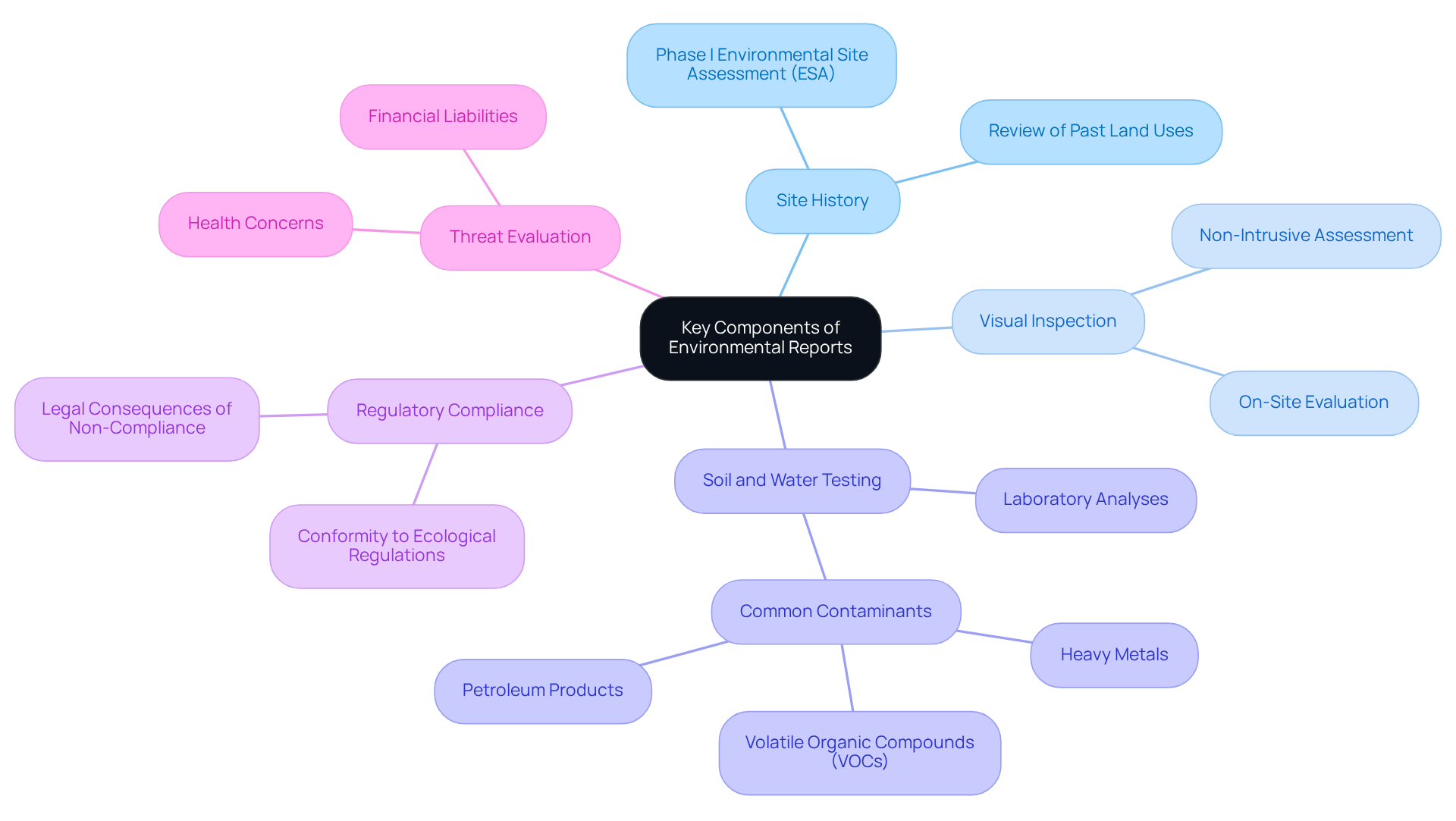
Identify Key Components of Environmental Reports
Key components of environmental reports include:
-
Site History: A thorough review of past land uses reveals potential contamination risks. Understanding the historical background of a site is essential, as it may unveil previous actions that could have resulted in ecological risks. A Phase I Environmental Site Assessment (ESA) is often required before acquiring commercial or industrial real estate, emphasizing the significance of an environmental report real estate in transactions.
-
Visual Inspection: A comprehensive evaluation of the premises and its surroundings is conducted to detect apparent indications of ecological risks. This step is vital for identifying issues that may not be evident through documentation alone. Notably, a Phase I ESA is nonintrusive, relying on historical research, on-site inspections, and interviews to assess the likelihood of contamination.
-
Soil and Water Testing: Laboratory analyses are performed to detect contaminants such as heavy metals, petroleum products, and hazardous waste. Common pollutants tested during Phase II ESAs include petroleum hydrocarbons, heavy metals, chlorinated solvents, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These tests are crucial for verifying the presence of contaminants that could impact both human health and the environmental report in real estate value. For instance, a Phase II Environmental Site Assessment (ESA) often includes soil and groundwater sampling to evaluate contamination levels.
-
Regulatory Compliance: This element assesses the property's conformity to local, state, and federal ecological regulations. Numerous regulations mandate assessments before construction or development, making compliance crucial for avoiding legal consequences and preserving the integrity of the investment.
-
Threat Evaluation: An analysis of the potential dangers posed by identified contaminants includes health concerns and financial liabilities. This assessment helps investors understand the implications of contamination and the necessary remediation efforts, which can be costly and time-consuming. For example, a case study highlighted how a REIT faced a $2 million decline in asset value due to soil contamination, emphasizing the significance of comprehensive ecological due diligence. Neglecting thorough assessments of ecological hazards can lead to unforeseen remediation expenses, legal breaches, and diminished property values.
Understanding these elements is crucial for real estate investors to make informed decisions and mitigate potential liabilities associated with ecological risks highlighted in the environmental report real estate.
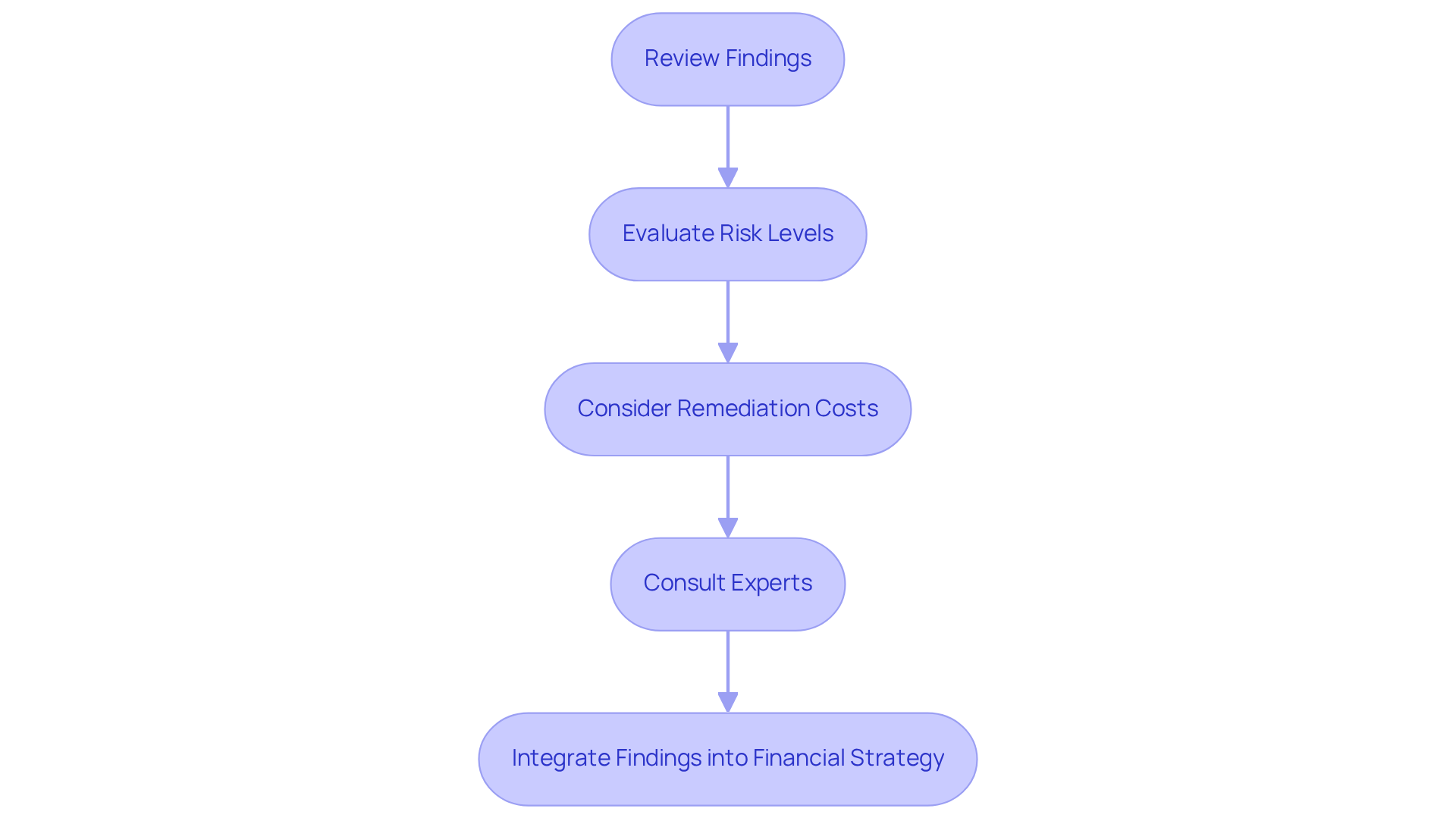
Analyze Environmental Reports for Real Estate Applications
To effectively analyze environmental reports, investors must follow these essential steps:
-
Review Findings: Investors should meticulously examine the results of soil and water tests, noting any contaminants present. Understanding the specific pollutants is crucial, as certain substances can significantly impact usability and marketability.
-
Evaluate Risk Levels: It is imperative to assess the severity of identified risks and their potential impact on asset value. For instance, assets with high levels of contamination may face considerable depreciation, while those with minor issues might only require slight adjustments. According to industry insights, properties with substantial ecological issues can experience value reductions of 20% or more.
-
Consider Remediation Costs: Estimating the financial implications of addressing ecological issues is vital, including cleanup and compliance costs. Average remediation costs can vary dramatically, often ranging from $10,000 to over $1 million, depending on the extent of contamination and the necessary cleanup methods. As financial analysts note, "The costs associated with remediation can drastically affect the overall investment return, making it essential for investors to factor these into their decision-making process."
-
Consult Experts: Engaging ecological consultants provides deeper insights into complex findings and recommendations for mitigation strategies. Their expertise can clarify the implications of the report and guide effective remediation planning. A case study from Zero Flux illustrates how a proactive approach to ecological concerns, highlighted in the environmental report real estate, led to successful redevelopment, significantly enhancing its market value.
-
Integrate Findings into Financial Strategy: Investors should leverage the insights gained from the report to inform critical financial decisions, such as negotiating purchase prices or determining property development plans. A well-informed strategy can yield improved financial outcomes and mitigate risks associated with ecological liabilities. Remember, real estate remains one of the most reliable avenues for building long-term wealth, and understanding these factors is vital for maximizing investment potential.
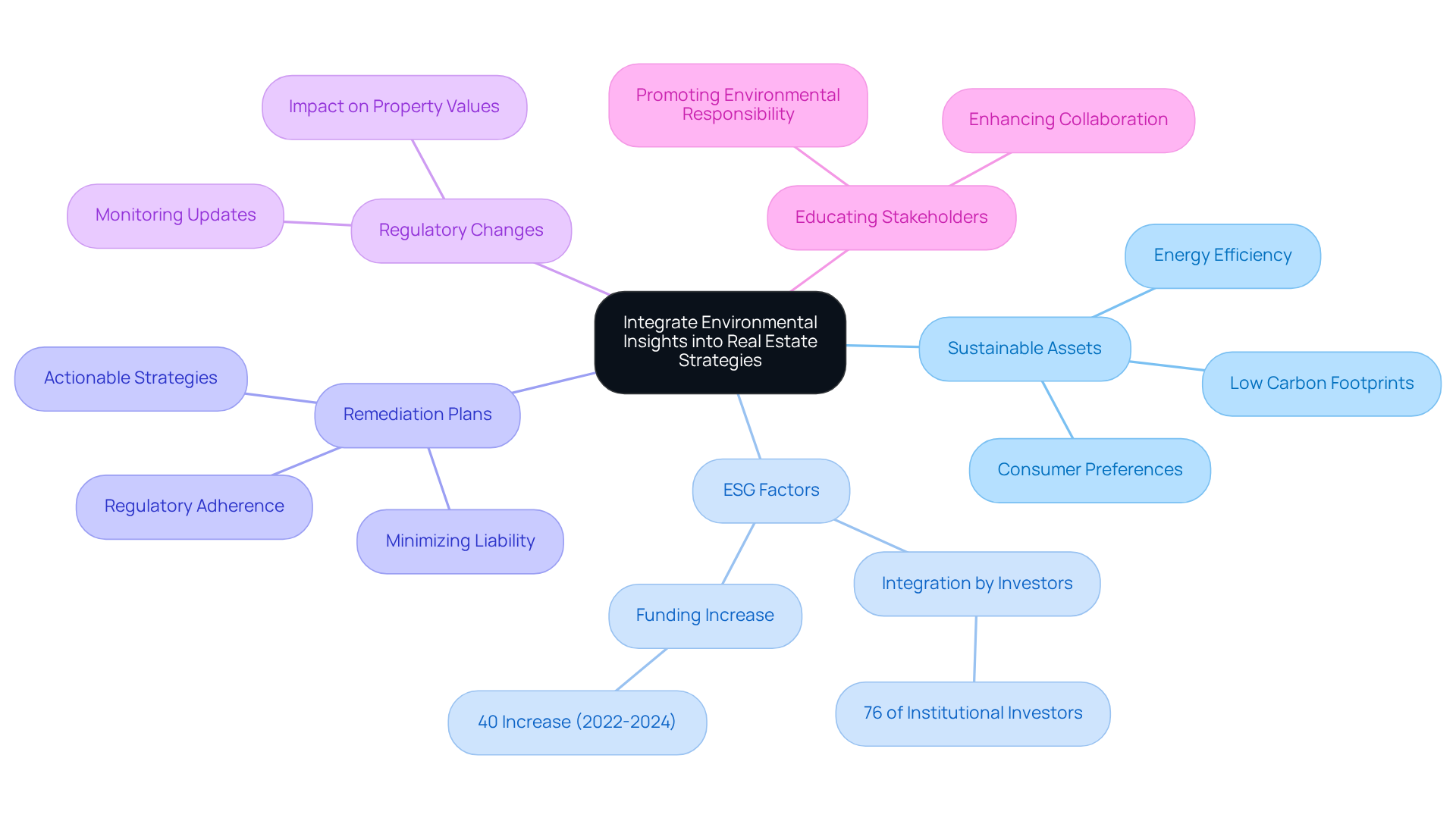
Integrate Environmental Insights into Real Estate Strategies
To effectively integrate environmental insights into real estate strategies, investors should:
-
Prioritize Sustainable Assets: Focus on assets with strong environmental credentials, such as energy efficiency and low carbon footprints. This approach aligns with growing consumer preferences and enhances long-term value, as properties with sustainable features are increasingly sought after in the market.
-
Include ESG Factors: Assess assets based on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria. A significant 76% of institutional investors now integrate these metrics into their decision-making processes, reflecting a shift towards sustainability that appeals to socially conscious investors. Recent data indicates that funding for projects aligned with ESG criteria increased by nearly 40% between 2022 and 2024, highlighting a robust market trend.
-
Develop Remediation Plans: Create actionable strategies for addressing any ecological issues identified in reports. This proactive strategy guarantees adherence to regulations and minimizes liability, ultimately protecting asset value as outlined in the environmental report real estate.
-
Monitor Regulatory Changes: Stay updated on changing ecological regulations that may affect property values and financial strategies. Understanding these dynamics is vital, as regulatory changes can greatly impact market conditions and the feasibility of capital allocation, especially in the realm of environmental report real estate.
-
Educate Stakeholders: Share insights with partners and stakeholders to promote a culture of environmental responsibility within funding practices. By fostering awareness and understanding of ESG factors, investors can enhance collaboration and drive sustainable outcomes in their portfolios.
Incorporating successful case studies of sustainable property investments can provide concrete examples of effective strategies. Quotes from ESG experts can further emphasize the importance of these practices, enriching the content and providing authoritative insights.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of environmental reports is crucial for real estate investors aiming to make informed decisions. These reports not only unveil potential ecological hazards but also serve as a foundation for assessing the viability and value of a property. By comprehensively analyzing factors such as soil, water, air quality, and regulatory compliance, investors can mitigate risks and enhance their investment strategies.
The article highlights several key components of environmental reports, including:
- Site history
- Visual inspections
- Soil and water testing
- Threat evaluations
Each of these elements plays a vital role in identifying potential liabilities that could affect property values. Furthermore, the importance of integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions is emphasized, showcasing a growing trend among investors who recognize the financial benefits of sustainable practices.
In conclusion, the significance of environmental reports in real estate cannot be overstated. As the industry shifts towards greater sustainability, investors must prioritize ecological assessments to protect their investments and align with market demands. By staying informed about regulatory changes and actively integrating environmental insights into their strategies, investors can not only safeguard their assets but also contribute to a more sustainable future in real estate.




