Overview
This article delves into the mastery of commercial real estate private equity (CREPE), presenting essential insights and strategies for investors in this dynamic sector. It highlights the potential for high returns and diversification benefits, underscoring the necessity of thorough market analysis. However, it does not shy away from addressing the inherent risks, including market fluctuations, illiquidity, and operational challenges. This comprehensive overview equips prospective investors with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of CREPE effectively.
Introduction
Navigating the intricate world of commercial real estate private equity (CREPE) presents a wealth of opportunities for savvy investors eager to diversify their portfolios and maximize returns. By pooling capital from various sources, CREPE facilitates direct investments in lucrative assets such as office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial properties, distinguishing it from traditional investment vehicles. As market dynamics evolve and sectors like industrial and multifamily housing gain traction, grasping the nuances of this investment strategy becomes essential.
This article delves into the following topics:
- The definition of CREPE
- The diverse types of commercial real estate investments
- Key factors for assessing opportunities
- The inherent risks and benefits
This provides a comprehensive guide for investors keen to capitalize on the evolving landscape of commercial real estate.
Define Commercial Real Estate Private Equity
Commercial real estate private equity represents a strategic investment avenue that pools capital from diverse investors to acquire, develop, and manage commercial property assets. In contrast to publicly traded real estate trusts (REITs), commercial real estate private equity facilitates direct real estate acquisitions, affording investors enhanced control and the potential for superior returns. Typically, participants in commercial real estate private equity comprise high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors who aim to benefit from the appreciation and income generated by commercial assets, including office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial facilities. This funding strategy is distinguished by its emphasis on value creation through proactive management and strategic enhancements to the assets involved.
Recent trends indicate a growing interest in CREPE, particularly as the retail sector's supply remains constrained, with projections suggesting it will not exceed 0.5% of current inventory in the near term. This limitation fosters a favorable environment for capital allocation, as it curtails new competition and allows existing assets to appreciate in value. Additionally, the real estate sector experienced an 11% increase in global deal value in 2024, reaching $707 billion, propelled by advantageous financing conditions and stabilization of asset values. This uneven recovery highlights the opportunities inherent in commercial real estate private equity, especially as investors increasingly focus on sectors yielding robust returns, such as data centers and alternative housing, signaling a shift towards higher-yield strategies and operational proficiency in commercial real estate private equity initiatives. Moreover, the ability to aggregate smaller capital contributions into substantial ventures revolutionizes property financing and management, making commercial real estate private equity an attractive option for a wide array of investors. As the sector evolves, integrating climate risk assessments into funding strategies has become increasingly vital, with the majority of participants acknowledging its moderate to significant incorporation. This trend emphasizes the importance for investors to account for environmental considerations when assessing potential commercial real estate private equity opportunities.
Explore Types of Commercial Real Estate Investments
Investments in commercial real estate private equity encompass a variety of categories, each characterized by unique investment profiles and potential returns:
- Office Buildings: Designed for business operations, these properties range from single-tenant structures to expansive multi-tenant complexes. They typically produce consistent cash flow through long-term leases, making them a dependable option. Analysts predict that office buildings will continue to adapt to changing work environments, emphasizing the importance of flexibility and modern amenities.
- Retail Spaces: This category includes shopping centers, malls, and standalone stores. While retail assets can be sensitive to economic fluctuations, prime locations often yield high returns, especially as consumer behavior evolves.
- Industrial Properties: Comprising warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities, industrial real estate has experienced significant growth, driven by the surge in e-commerce and logistics demands. Statistics suggest that this sector is anticipated to gain a larger market share in 2025, demonstrating its growing significance in the financial landscape.
- Multifamily Housing: Apartment complexes and multi-unit residential buildings fall under this category, providing consistent rental income. They are frequently considered more secure assets due to the persistent demand for housing, with forecasts indicating a sustained increase in this sector's market share.
- Hospitality: Encompassing hotels and resorts, this sector can be lucrative but is also subject to market volatility and seasonal demand variations, requiring careful market analysis.
- Mixed-Use Developments: These properties integrate residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial spaces, offering diversified income streams and appealing to a broad range of tenants.
- Special Purpose Properties: This encompasses distinctive assets like schools, churches, and self-storage facilities, which may require specialized knowledge for effective assessment and funding.
- Vacant Land: Investing in undeveloped land can be speculative but holds the potential for significant appreciation as demand increases, particularly in growing areas.
As of 2025, the market share of these investment types reflects shifting priorities, with sectors like industrial and multifamily housing gaining traction. When questioned regarding the best prospects in property over the next 12 to 18 months, high-growth sectors such as industrial and multifamily emerged as top priorities, indicating where property owners and investors may find the greatest potential for returns. Grasping these dynamics is crucial for investors in commercial real estate private equity who aim to maneuver through the commercial property landscape efficiently.
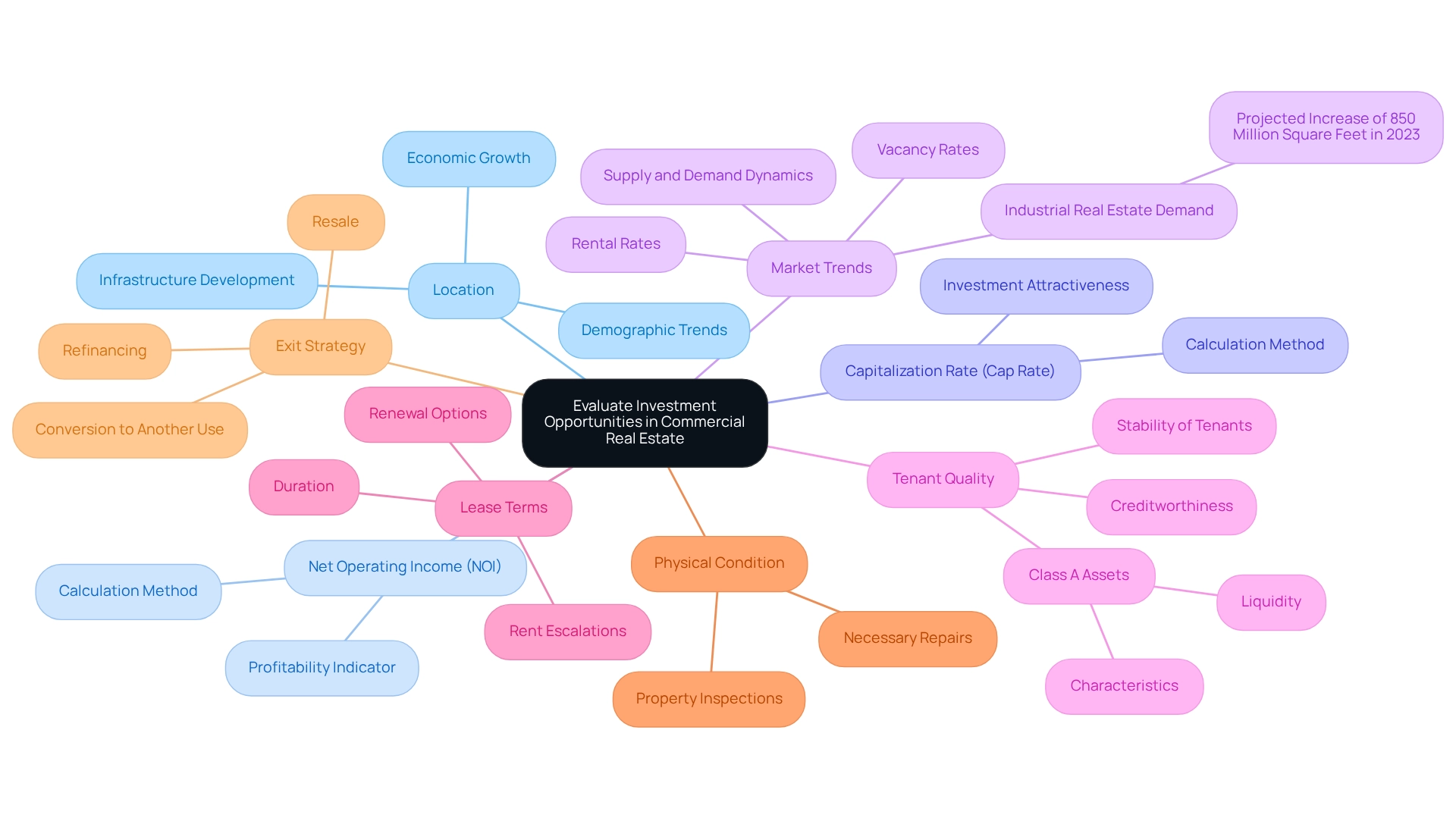
Evaluate Investment Opportunities in Commercial Real Estate
To effectively evaluate investment opportunities in commercial real estate, investors must consider several key factors:
- Location: The site's position is paramount. Analyzing the surrounding area for economic growth, infrastructure development, and demographic trends is essential. As Jesse Jones, a business owner, emphasizes, 'the basis of wealth resides in the land itself,' underscoring the vital significance of choosing the right site for capital allocation.
- Net Operating Income (NOI): Calculate the NOI by subtracting operating expenses from gross rental income. This metric is essential for evaluating the asset's profitability and grasping its financial health.
- Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate): The cap rate, determined by dividing the NOI by the property's acquisition cost, offers insight into the anticipated return. A higher cap rate typically indicates a more attractive investment opportunity.
- Market Trends: Staying informed about local and national market trends, including supply and demand dynamics, rental rates, and vacancy rates, is vital. For instance, the demand for industrial real estate in the U.S. is projected to rise by 850 million square feet in 2023, highlighting a significant opportunity in that sector. Additionally, as we look towards 2025, average net operating incomes are expected to shift, making it essential for investors to monitor these changes closely.
- Tenant Quality: Evaluating the creditworthiness and stability of existing tenants impacts cash flow and risk. Strong tenants contribute to consistent income and lower vacancy rates. Class A assets, characterized by contemporary structures in prime locations with long-term leases, are viewed as highly liquid investments in commercial real estate private equity due to their stable cash flows and strong market demand, making them particularly attractive to investors.
- Lease Terms: Reviewing lease agreements for duration, renewal options, and rent escalations can affect long-term income stability. Favorable lease terms can enhance the appeal of the asset to investors.
- Physical Condition: Conduct thorough inspections to assess the property's condition and identify any necessary repairs or upgrades. Properties in good condition are more likely to attract quality tenants and maintain value.
- Exit Strategy: Consider potential exit strategies, including resale, refinancing, or conversion to another use, to maximize returns. A well-defined exit strategy can significantly influence investment decisions and outcomes.
In 2025, grasping these elements will be essential as the business property landscape continues to evolve. Successful investors learn from both good and bad experiences, making informed decisions based on comprehensive analysis.
Analyze Risks and Benefits of Commercial Real Estate Private Equity
Investing in commercial real estate private equity (CREPE) offers a distinctive combination of risks and benefits that investors must thoroughly assess:
Benefits:
- Potential for High Returns: The potential for high returns in commercial real estate private equity (CREPE) often yields substantial returns through property appreciation and rental income, frequently surpassing conventional financial options. Greater wealth has been created in property than in all industrial ventures combined, underscoring its profitable potential.
- Diversification: Incorporating commercial real property into a financial portfolio can mitigate overall risk by diversifying asset categories, providing a buffer against market fluctuations.
- Professional Management: Investors benefit from the expertise of professional managers who oversee asset operations, alleviating the operational burden on individual investors and enhancing overall performance.
- Tax Advantages: Real estate holdings typically offer tax benefits, such as depreciation and the potential for 1031 exchanges, which can significantly enhance net returns.
Risks:
- Market Risk: Economic downturns can adversely affect real estate values and rental income, potentially leading to substantial losses.
- Illiquidity: Assets in commercial real estate private equity are generally less liquid than stocks or bonds, complicating quick access to funds when needed.
- Operational Risks: Ineffective asset management or unforeseen maintenance issues can diminish profits, highlighting the importance of selecting skilled management teams.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in zoning laws, tax policies, or environmental regulations can influence real estate values and financial returns, necessitating vigilance in regulatory compliance.
- Leverage Risks: Many CREPE investments employ debt to finance acquisitions, which can amplify losses if asset values decline, underscoring the need for prudent financial strategies.
As investors navigate the complexities of commercial real estate private equity in 2025, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed decisions. Financial analysts stress that choices should be based on knowledge rather than speculation, reinforcing the significance of thorough market analysis and strategic planning. Jesse Jones, a business owner, aptly stated, "I have always liked property; agricultural land, grazing land, forest land, and urban property. I have had experience with all of them. I guess I just naturally like ‘the good Earth,’ the foundation of all our wealth." This perspective highlights the enduring value of property holdings.
Furthermore, as we approach the second quarter of 2025, investors must remain adaptable and well-informed to navigate the swiftly evolving economy. Grasping financing options is essential for aligning capital strategy with investment objectives, encompassing conventional loans, government-backed programs, and short-term bridge financing. Access to appropriate financing can significantly influence the success of commercial real estate transactions, facilitating effective deal structuring.
Conclusion
The exploration of commercial real estate private equity (CREPE) uncovers substantial potential for investors aiming to diversify their portfolios and achieve elevated returns. Understanding the definition of CREPE and its various categories of commercial real estate investments enables investors to pinpoint opportunities in sectors such as office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial properties. Each category boasts distinct characteristics and growth prospects, underscoring the necessity of strategic investment choices tailored to prevailing market conditions.
Evaluating investment opportunities mandates a thorough analysis of critical factors, including:
- Location
- Net operating income
- Tenant quality
Additionally, market trends and lease terms significantly influence the viability of an investment. As the commercial real estate landscape continues to evolve, investors must remain vigilant and well-informed to navigate potential risks, including market fluctuations and operational challenges.
Ultimately, the advantages of investing in CREPE—such as high return potential and professional management—must be carefully weighed against the inherent risks. By adopting a well-informed approach grounded in meticulous analysis, investors can seize the lucrative opportunities present within the commercial real estate sector. As the market persists in its shifts and adaptations, staying ahead of trends and maintaining a strategic mindset will be essential for achieving success in this dynamic investment landscape.




