Overview
The article delves into mastering real estate amortization, elucidating its key concepts and calculations. Understanding amortization is crucial for effective financial management in real estate, and this piece emphasizes its significance. It explains the workings of amortization through both fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages, detailing calculation methods and the influence of amortization schedules on investment strategies. By doing so, it equips readers with the essential knowledge required for informed decision-making in real estate financing.
Introduction
In the intricate world of real estate financing, understanding amortization is not merely beneficial—it is essential. This systematic approach to settling loans through regular payments empowers homeowners and investors alike, enabling effective management of cash flow and equity building.
However, with various loan types and fluctuating interest rates complicating the landscape, how can one navigate these complexities to make informed financial decisions?
This article delves into the key concepts and calculations of real estate amortization, providing insights that can significantly impact investment strategies and long-term financial health.
Define Amortization in Real Estate
The systematic method of gradually settling a loan through regular contributions over a specified duration is known as real estate amortization. Each payment comprises both principal and interest, with the principal amount diminishing over time. This structured reduction of debt is crucial for both homeowners and investors, as it not only aids in managing cash flow but also facilitates the accumulation of equity in the property. Understanding real estate amortization is vital for making informed decisions regarding loan options and investment strategies, ultimately empowering readers to navigate the complexities of real estate financing effectively.
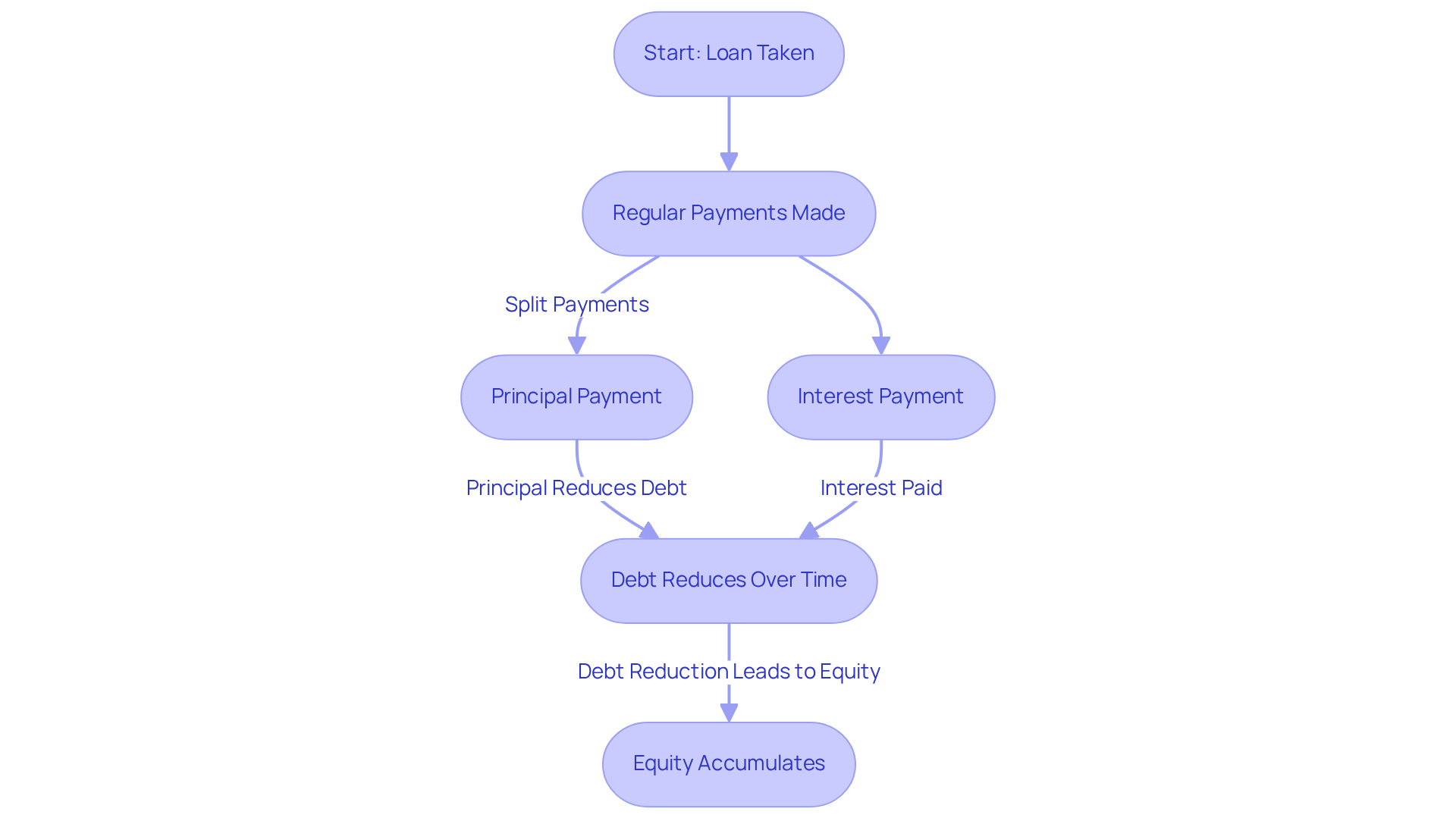
Explain Amortization in Real Estate Loans
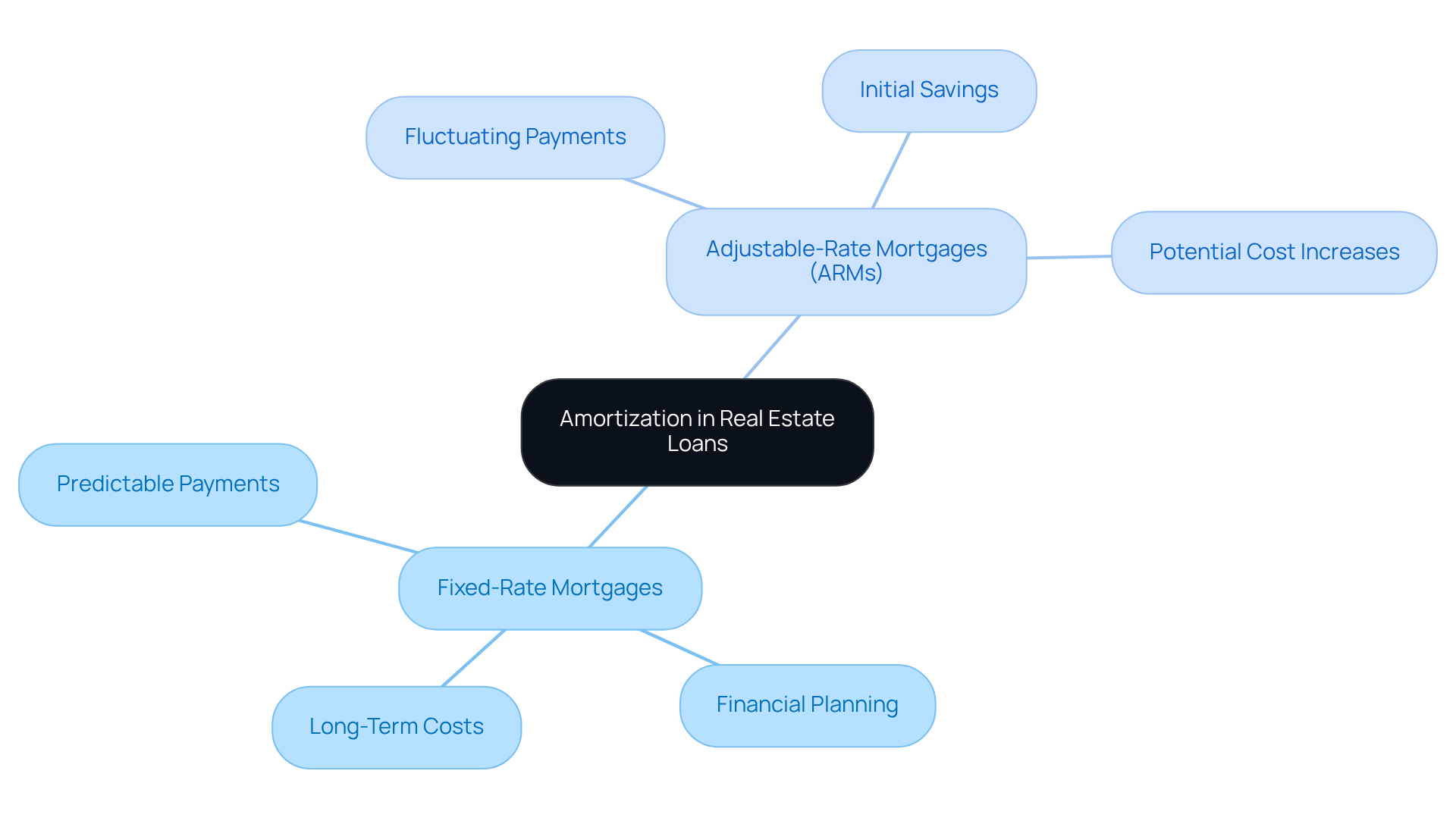
In the realm of real estate loans, real estate amortization is primarily organized through fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs). A fixed-rate mortgage offers a steady cost throughout the loan's duration, resulting in predictable monthly expenses. This stability empowers borrowers to plan their finances effectively, as they can anticipate their payments with certainty. Conversely, ARMs feature fluctuating interest rates that can change at designated intervals, directly impacting the amortization schedule. As interest rates rise or fall, so do the monthly payments, leading to variations in long-term financial obligations.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for borrowers, as they significantly shape overall investment strategies related to real estate amortization. For instance, while fixed-rate mortgages provide certainty and predictability, ARMs may offer lower initial costs, potentially leading to substantial savings during the early years of the loan. However, this can culminate in higher expenses later, particularly if market rates increase. A recent case study highlighted that homeowners with ARMs could see their costs escalate from $1,181 to $1,637 by 2025, underscoring the financial implications of selecting an ARM.
Amortization schedules for real estate amortization also differ based on the loan term, typically ranging from 15 to 30 years. Shorter durations generally result in higher monthly payments but lower overall expenses throughout the loan's life. In contrast, extended terms spread payments over additional months, reducing monthly costs while increasing the total amount paid. For example, a homeowner with a 30-year fixed loan may incur significantly higher fees compared to a borrower with a 15-year loan, even if the charges remain the same.
Current trends suggest that as of 2025, home loan interest rates are fluctuating, prompting many borrowers to weigh the benefits of fixed-rate versus adjustable-rate options. Recent data indicates that ARMs constituted approximately 10% of new loan originations, reflecting a cautious shift in consumer behavior as homeowners strive to balance initial savings with long-term financial stability. Furthermore, the staggering figure of $12.61 trillion owed by Americans on 85.10 million home loans emphasizes the necessity of understanding amortization amidst such considerable debt levels. The 28 percent rule advises that no more than 28 percent of gross monthly income should be allocated to housing costs, serving as a practical guideline for evaluating mortgage affordability. Grasping the nuances of real estate amortization in loans is vital for making informed decisions that align with individual financial objectives.
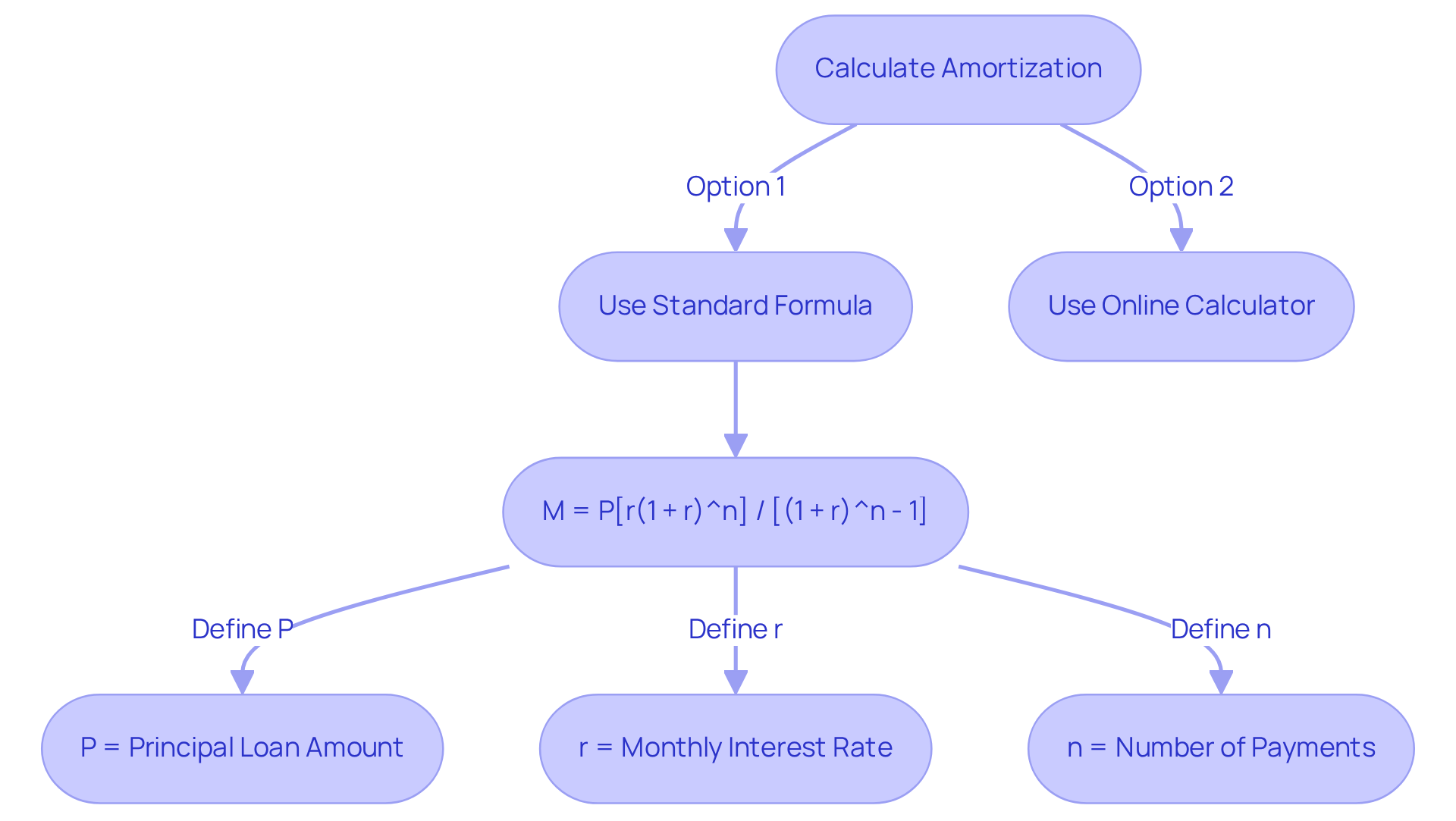
Calculate Amortization: Methods and Tools
Calculating real estate amortization is essential for anyone navigating the real estate landscape. One can employ various methods, including the standard amortization formula or user-friendly online calculators. The fundamental formula for determining the monthly payment (M) is as follows:
M = P[r(1 + r)^n] / [(1 + r)^n - 1]
Where:
- P = principal loan amount
- r = monthly interest rate (annual rate divided by 12)
- n = number of payments (loan term in months)
Alternatively, many online tools and calculators simplify this process, delivering comprehensive amortization schedules that detail how each payment is allocated toward principal and interest. Leveraging these tools enables investors and homeowners to visualize their financial structure effectively, including real estate amortization, empowering them to plan their investments with greater confidence.
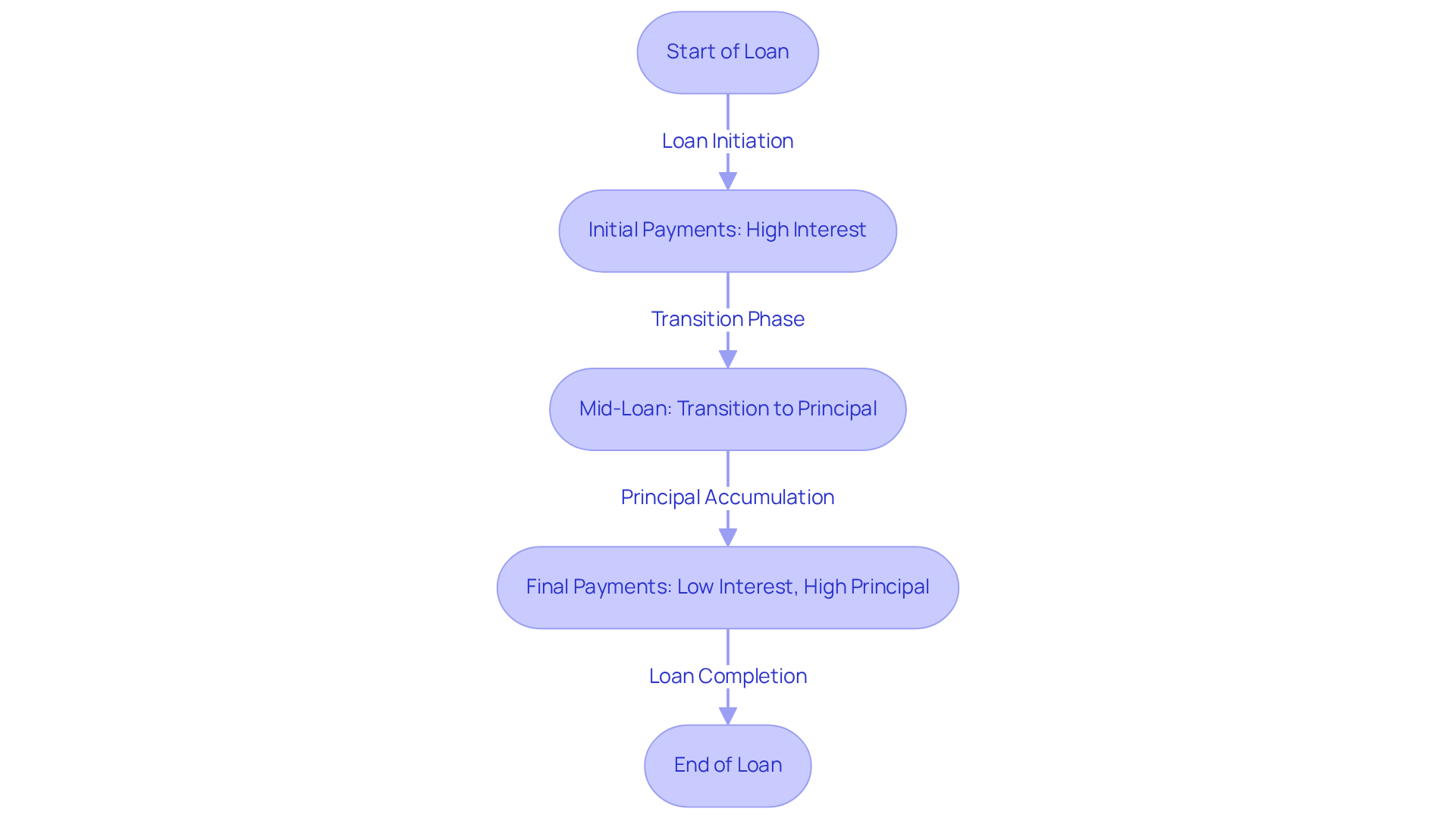
Analyze Amortization Schedules and Investment Impact
Amortization schedules provide a comprehensive overview of each installment throughout the loan's term, detailing the distribution between charges and principal. This analysis is crucial for investors aiming to maximize their returns, as it highlights the pace at which equity accumulates in a property.
In the early years of a loan, a significant portion of each installment is allocated to costs, while later payments progressively reduce the principal amount. For example, a $200,000 mortgage at a 5% interest rate results in monthly payments of approximately $1,073.64, illustrating the interest-heavy nature of early payments. This shift can significantly affect an investor's cash flow and strategic decisions, particularly concerning refinancing or property sales.
As Sarah Lee notes, "Amortization schedules provide clarity on future liabilities, enabling businesses to forecast cash flow requirements." Understanding these dynamics is essential for making informed choices in real estate investment, as effective management of amortization can lead to substantial long-term financial benefits.
Conclusion
Understanding real estate amortization is crucial for anyone involved in property financing, whether as a homeowner or an investor. This systematic approach to loan repayment allows individuals to manage their cash flow effectively while building equity over time. By grasping the intricacies of amortization, one can navigate the complexities of real estate financing and make informed decisions that align with their financial objectives.
Throughout this article, key concepts have been explored, including:
- The definitions and types of amortization in real estate loans
- The differences between fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages
- The significance of amortization schedules
Additionally, methods for calculating amortization have been discussed, along with the impact these calculations can have on investment strategies and long-term financial stability. Recognizing how these components interact is vital for managing substantial debt and maximizing returns on real estate investments.
In conclusion, the importance of mastering real estate amortization cannot be overstated. As interest rates fluctuate and the real estate landscape evolves, staying informed about amortization strategies is essential for making sound financial decisions. Whether considering a mortgage or evaluating investment opportunities, a thorough understanding of amortization can lead to better financial outcomes and a more secure future in real estate. Embrace the knowledge gained here to empower financial planning and enhance investment success.




