Overview
This article presents a comprehensive guide to mastering self-directed 401(k) real estate investments, focusing on the flexibility and potential benefits inherent in this investment strategy. It begins by outlining the essential steps for setting up a self-directed 401(k), which is crucial for maximizing investment opportunities. The discussion then highlights the advantages of investing in real estate, including potential returns and diversification benefits.
Practical guidance for purchasing properties is also provided, ensuring readers are well-equipped to make informed decisions. Importantly, the article underscores the necessity of compliance with IRS regulations, which is vital for maximizing financial growth and avoiding penalties.
By following these steps, investors can effectively navigate the complexities of self-directed 401(k) real estate investments and harness their full potential.
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of retirement planning, the Self-Directed 401(k) stands out as a powerful tool for those determined to transcend conventional investment options. This innovative retirement savings plan empowers individuals to take control of their financial futures while unveiling a wealth of investment possibilities, including real estate and private equity.
As an increasing number of self-employed individuals recognize the potential advantages of this flexible account structure, a comprehensive understanding of its intricacies becomes essential. From the regulatory framework to the strategic benefits of investing in real estate, this article explores the myriad opportunities and necessary steps to fully harness the power of a Self-Directed 401(k) for a prosperous retirement.
Understand the Self-Directed 401(k) Basics
A self-directed 401(k) real estate plan is a flexible retirement savings option that empowers you to make investment choices beyond the constraints of traditional stocks and bonds. Unlike standard 401(k) plans, which typically restrict you to mutual funds and similar options, a self-directed 401(k) real estate plan opens the door to a wider array of assets, including real estate, private equity, and more. To qualify for this type of account, you must be self-employed or own a business without any full-time employees aside from yourself and possibly your spouse.
Understanding the rules and regulations governing 401(k) accounts managed by individuals is crucial, as these dictate allowable investments and fund usage. Recent data reveals a growing trend among self-employed individuals opting for individual 401(k) plans, signaling a shift towards more personalized retirement strategies. In 2024, the average IRA contribution rose to $1,500, reflecting an increasing commitment to retirement savings, likely mirrored in the 401(k) landscape.
Moreover, the typical 401(k) plan fee was recorded at 0.46% of assets in 2020, highlighting the cost-effectiveness of individually managed 401(k) plans compared to conventional options. It's also important to note that in 2020, 48% of employees in the US reported not saving for retirement, emphasizing the need for diverse retirement savings alternatives such as individually managed 401(k) plans. Navigating the complexities of these accounts necessitates a thorough understanding of the relevant regulations, ensuring compliance while maximizing financial potential.
This information is vital for anyone looking to leverage a self-directed 401(k) real estate plan for property investments, as it supports strategic planning and informed decision-making.
Explore the Benefits of Investing in Real Estate with a Self-Directed 401(k)
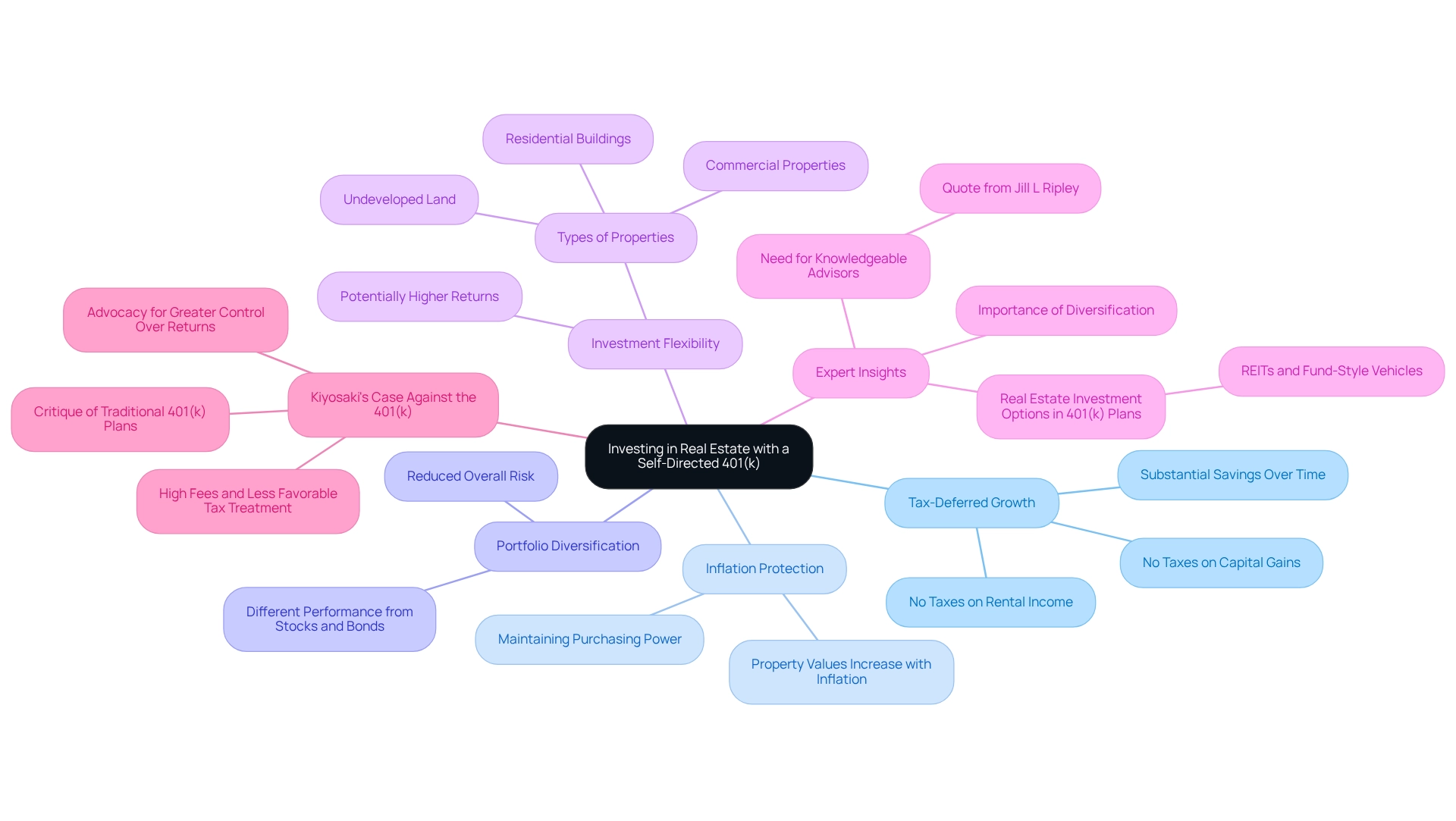
Investing in real property through a self-directed 401k real estate option presents numerous advantages that can significantly enhance your financial strategy. One of the primary benefits is tax-deferred growth; you won't incur taxes on rental income or capital gains until you withdraw funds during retirement. This deferral can lead to substantial savings over time, allowing your investments to compound more effectively.
Moreover, property acts as a strong safeguard against inflation. As property values and rental income generally increase with inflation, investing in real assets can help maintain your purchasing power. Furthermore, broadening your portfolio with property holdings can reduce overall risk, as these assets frequently perform differently than conventional stocks and bonds.
The flexibility of a self-directed 401k real estate plan enables you to invest in various types of property, including residential buildings, commercial properties, and even undeveloped land. This versatility not only enhances your financial strategy but also opens up opportunities for potentially higher returns compared to traditional financial vehicles.
Statistics indicate that a property valued at $180,000 could result in a depreciation figure of $45,000, further demonstrating the tax benefits related to real estate ventures. Furthermore, contributions to IRAs are limited to $7,000 annually for individuals under 50 and $8,000 for those 50 and older in 2025, making it a favorable time to explore these financial options.
Expert insights highlight the importance of diversification in self-directed 401k real estate investments. As highlighted by industry experts, diversifying your assets can result in more stable returns and decreased volatility. Jill L Ripley, a property agent, raises an important question: "Who would you contact to arrange something like this?" Are most financial advisors aware of these things? This underscores the need for investors to seek knowledgeable advisors who understand these options.
Moreover, Brock highlights that numerous 401(k) plans provide property financing options through real property trusts (REITs) and other fund-style vehicles, offering extra pathways for funding within conventional plans. This context is crucial for readers considering their choices.
This method corresponds with Robert Kiyosaki's critique of conventional 401(k) plans, where he contends that they frequently involve high fees and less advantageous tax treatment compared to self-directed 401k real estate ventures. By utilizing a Self-Managed 401(k), investors can gain greater control over their returns and potentially improve their overall financial results.
Set Up Your Self-Directed 401(k) for Real Estate Investment
To establish your Self-Directed 401(k) for real estate investments, follow these essential steps:
- Determine Eligibility: Confirm your eligibility by ensuring you are self-employed or own a business without full-time employees. This foundational step is critical to setting the stage for your investment strategy.
- Choose a Provider: Select a reputable financial institution that specializes in individual-managed 401(k) plans. Investigate their fees, services, and overall reputation to find the best fit for your needs. Remember, the commitment to quality content enhances subscriber engagement and authority in the industry; choose wisely.
- Complete the Application: Fill out the required application forms to set up your account. This procedure typically entails supplying personal information, business specifics, and your financial preferences, laying the groundwork for your investment journey.
- Fund Your Account: Fund your Self-Directed 401(k) through contributions, rollovers from existing retirement accounts, or transfers. Be mindful of contribution limits and the associated tax implications to optimize your financial strategy. According to Fidelity, the average IRA contribution was $1,500, up from $1,300 in the third quarter of 2023. This highlights the importance of maximizing your contributions to enhance your retirement portfolio.
- Establish a Financial Plan: Create a clear financial plan that specifies how you will distribute your resources, with an emphasis on property opportunities that align with your financial goals. Engaging with financial professionals can help individuals strategize and address gaps in their retirement savings and income plans, as illustrated in the case study titled "Leveraging Financial Resources."
By following these steps, you can effectively utilize your Self-Directed 401(k) for real estate to improve your property portfolio. Stay informed through resources like Zero Flux, which compiles 5-12 curated insights on real properties daily, ensuring you remain ahead in your investment strategy.
Follow the Steps to Purchase Real Estate with Your Self-Directed 401(k)
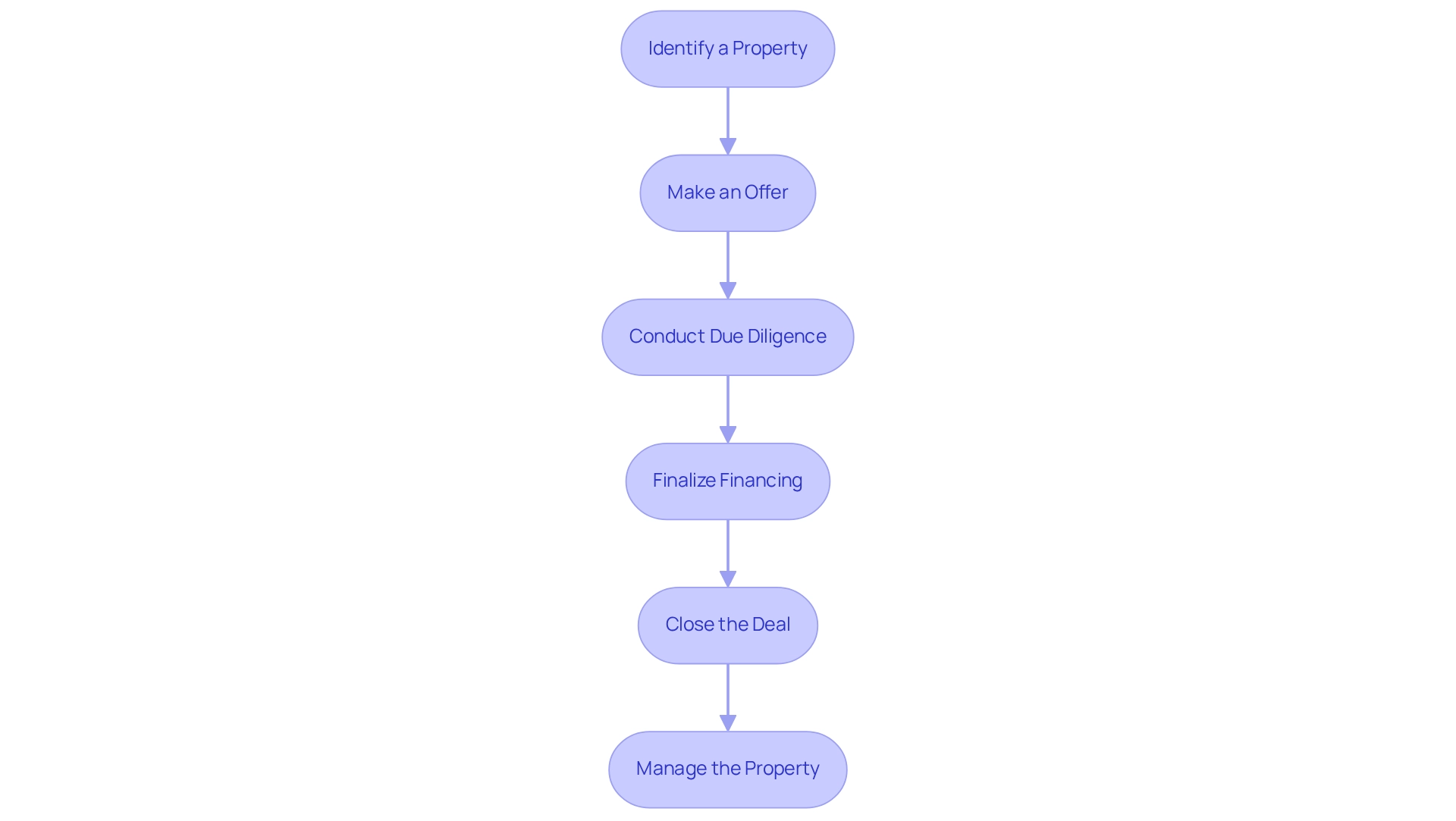
To acquire real property with your Self-Directed 401(k), follow these essential steps:
- Identify a Property: Conduct thorough research to select a property that aligns with your financial objectives. Key considerations include location, potential rental income, and prevailing market trends. Remember, real estate ventures have the potential for growth, as properties can increase in value over time.
- Make an Offer: Once you identify a suitable property, submit an offer. It is essential that the offer is made in the name of your 401(k) plan rather than your personal name to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
- Conduct Due Diligence: Engage in comprehensive due diligence on the property. This includes inspections, appraisals, and title searches to uncover any potential issues that could affect your investment. Consulting with professional advisors during this process is highly recommended to navigate the complexities involved.
- Finalize Financing: If financing is necessary, ensure it adheres to IRS guidelines. Typically, only non-recourse loans are allowed for real property acquisitions within a 401(k) plan.
- Close the Deal: Collaborate with a real estate attorney or closing agent to finalize the transaction. Ensure that all funds are properly transferred from your personal 401(k) to complete the purchase.
- Manage the Property: After acquiring the property, manage it in accordance with IRS rules. All income produced must be reinvested into your 401(k), and personal use of the property is not allowed. Gains from selling properties or receiving rental revenue through an SDIRA can increase tax-deferred until withdrawal during retirement.
By adhering to these steps, investors can successfully navigate the intricacies of acquiring real property through a Self-Directed 401(k), optimizing their financial potential while complying with regulatory standards. Including insights from real estate professionals on conducting due diligence can further enhance your approach to these investments.
Conclusion
The Self-Directed 401(k) offers a transformative opportunity for self-employed individuals aiming for a dynamic approach to retirement planning. By enabling a broader spectrum of investment options—including real estate and private equity—this plan empowers investors to take control of their financial futures. Understanding the fundamentals, such as eligibility requirements and regulatory compliance, is crucial for maximizing the benefits of this versatile retirement savings tool.
Investing in real estate through a Self-Directed 401(k) presents significant advantages, including tax-deferred growth, inflation protection, and the potential for higher returns. By diversifying portfolios with real estate, investors can effectively mitigate risks associated with traditional investments. As the landscape of retirement savings continues to evolve, the importance of informed decision-making and strategic planning cannot be overstated. Engaging with knowledgeable financial advisors can provide essential insights and support throughout the investment process.
In summary, establishing and managing a Self-Directed 401(k) for real estate investment involves a series of well-defined steps, from determining eligibility to finalizing property purchases. By adhering to the outlined procedures and leveraging the unique advantages of this retirement account, individuals can build a robust and resilient investment portfolio. As more self-employed individuals recognize the potential of Self-Directed 401(k) plans, they can pave the way toward a prosperous retirement while enjoying the freedom to explore diverse investment opportunities.




